Any hydraulic heating system is a complex of heating devices and heating devices connected to each other by a pipeline in in a certain order. When the coolant is heated, it changes in volume (expands). A closed heating system with forced circulation provides compensation for this process due to expansion tank.
Depending on whether such a tank communicates with the external atmospheric air, heating systems are divided into two types - open and closed heating systems.
The coolant circulates using a pump. The inclusion of a pump in the hydraulic circuit allows heating of rooms more efficiently. Forced circulation allows you to include additional heating devices in such a scheme (for example, “warm floor” systems).
The presence of a pump in the circuit makes heating dependent on the power supply, but at the same time the circulation of the coolant is much more efficient.
When implementing such a scheme, the installation of this pump is carried out on the return main pipe in front of the boiler. An expansion tank for heating is also installed there. closed type.
It is clear that this arrangement makes the installation itself simpler, since there is no need to maintain the slope angle, insulate the pipeline and install larger diameter pipes on the main risers (mains) (which is not always aesthetically pleasing in a residential area).

A closed heating system prevents evaporation of the coolant. In this regard, there is no need to constantly monitor its level in the system.
Forced circulation of the coolant allows you to warm up in less time and change the heating in each individual room. If a room thermostat is included in the circuit, then it becomes possible to effectively heat the rooms when the temperature changes below the set one.

Heating circuit elements
A closed-type heating circuit includes the following elements:
- , solid fuel, etc.);
- membrane expansion sealed tank;
- circulation pump;
- radiators and radiators;
- pipes for riser lines, connections and jumpers;
- fittings (pipe adapters);
- taps (plug and ball) and valves (Mayevsky systems);
- filters (mainly to maintain the operation of the boiler);
- fasteners (clamps, etc.).
Principle of operation
- The coolant (water or antifreeze) is heated in heating boiler
. As the temperature of the medium increases, the volume increases.
Excess coolant goes into the expansion tank, which in appearance resembles a capsule divided into two compartments.
One compartment is a hydraulic chamber into which the coolant liquid flows when heated. The second compartment is a gas chamber, which is filled with nitrogen under a certain pressure;

- Before heating starts, a pressure is established in the tank equal to hydrostatic pressure in the circuit. When the coolant is heated, it enters the expansion tank through the valve.
Due to this, the pressure inside the system is equalized (since the volume of the gas chamber decreases and the gas pressure increases). From the expansion tank, the coolant is returned to the system by the same circulation pump.
Design features of a closed heating system
The heating circuit with forced circulation of a closed type has some features. The expansion tank and circulation pump can be placed in the same room together with the heating boiler.
This provides a number of advantages - the total length of pipelines is reduced, and there is no need to install pipes large diameter and compliance with inclination angles during installation.

The hermetically sealed design of this type of expansion tank prevents evaporation of coolant from the system and airing of pipelines.
Important!
A membrane-type expansion tank and a circulation pump must be installed on the return main pipe.
The pump can be operated longer if a fluid flows through it at a lower temperature.
The open type of heating circuit has certain size restrictions, so it can only be used in small rooms. Closed heating does not have such restrictions.
Advantages and disadvantages of a closed heating system
A sealed forced circulation heating system of a closed heating type has its pros and cons. It has more advantages, so they should be considered in more detail, although there are also negative aspects.
Advantages of a closed heating system
- Great heat transfer;
- No coolant evaporation;
- Possibility of using pipes of smaller diameter;
- The service life of the boiler is longer due to the reduction in the temperature difference at the inlet and outlet;
- Reduced corrosion due to tightness;
- Possibility of using antifreeze as a coolant.
Disadvantages of a closed heating system
- Volatility dependence (requires power supply for);
- The volume of the expansion tank should be much larger; naturally, it is somewhat more expensive.
Conversion of an open system with natural circulation to a closed one
The closed option is a method of equipping a heating system without circulation pump. In practice, this type of heating organization is extremely rare, but its performance is not in doubt.

As a rule, it is not specifically designed initially in this form, but when you replace a conventional expansion tank with a membrane one with your own hands, it turns from an open system with natural circulation closed with natural circulation.
It goes without saying that it is possible to calculate, design and assemble such a system in advance, but at the same time many of obvious advantages closed systems are lost. For example, you need to very accurately calculate the diameters of risers and mains, lay pipes at an angle, and air pockets will form.
The advantage that natural circulation gives in a closed heating system is independence from the power supply.
Is such a dubious advantage worth the specific disadvantages? It is unlikely that anyone would think of building housing with water heating, but without electricity. The price of a regular pump is about one hundred dollars. At the same time, it takes electricity, like an incandescent light bulb from table lamp– 40-60 W.
You can see how to install it correctly in the video:
Heating system installation
Installation closed system heating starts with choice suitable boiler according to two criteria - the type of boiler and its power. IN Lately gaining popularity solid fuel boilers. Although they are more cumbersome, they are cheaper to operate. The power of the boiler depends on many factors.
Important!
How should power be calculated? The calculation instructions assume the following: with a ceiling height of up to three meters, average insulation of a two- or three-story private house, 1 kW of heating boiler power is required to heat every 10 m2.
As practice shows, the price of such a boiler is about 1,000 US dollars.
The type of heating devices (heating radiators or radiators) is selected based on the available funds. All types of radiators give off heat approximately equally, and their service life is also not very different. If we stop at steel radiators, then their cost for such a house will also be about 1,000 US dollars.
- pipes – 500;
- pump – 100;
- tank – 50;
- fittings, taps, filters – 500;
- design and installation – another 1,000.
In total, the very approximate cost of installing a closed heating system in a private house will cost 1,000+1,000+500+100+50+500+1000 = 4,150 US dollars.

So, the equipment has been installed, the pipes have been laid. It is possible to fill a closed heating system with water.
conclusions
Taking into account the pros and cons that a closed heating system with natural circulation has, and roughly estimating the cost of installing a system with forced circulation, we can conclude that there is no fundamental difference between such systems. The only thing that can be said is that a system with forced circulation is more profitable from an installation point of view and the equipment in it lasts longer.
In the private sector within the city or outside it, there is no possibility of connecting the house to central heating, so cottage owners are engaged in installation autonomous heating. Installation of open and closed heating systems is possible
Autonomous heating is a system of interconnected elements that heat up when connected to a heat source. It can be either stove or water or electric heating– it all depends on whether the residents are there permanently or come periodically.
Properly installed water heating can be powered from any energy source - gas, solid fuel, development.
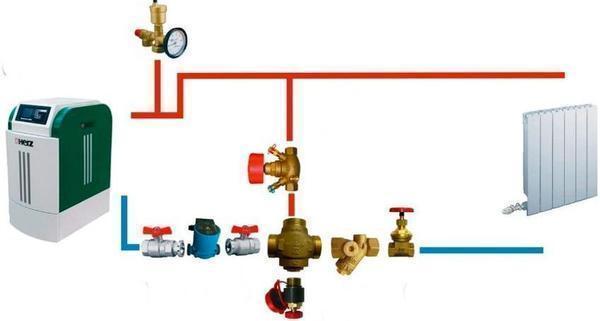
The closed-type heating supply consists of pipes, a boiler, a circulation pump, a battery and an expansion tank. All elements are sealed - water does not evaporate when heated and circulated.
Differences between closed and open heating systems:
- Open autonomous system heating system involves installing an expansion tank in the highest place - in the attic under the roof; when closed, it can be placed anywhere.
- Unlike an open one, a closed heating system is sealed and isolated from air flows.
- An open heating system uses wide pipes that are installed at a certain angle for better circulation. A closed system requires smaller diameter pipes.
- For a closed heating system, it is important to install and adjust the pump correctly.
Circulation pumps ensure uniform distribution of coolant through the pipes, increase system productivity and help save fuel consumption.
Closed heating system: advantages and disadvantages
A sealed heating system with a pump operates under pressure and in complete atmospheric isolation, which leads to less oxidation of metal elements.
Pros of the system:
- The coolant is water, it does not evaporate, it is constantly in the system. If necessary, antifreeze can be used, which allows the system not to freeze, even if it is turned off for a short period.
- Using a pump to circulate the coolant allows the system to operate faster and, accordingly, heat the room faster.
- The expansion tank can be placed in close proximity to the boiler, which makes the system more compact.
- Using special taps, you can adjust the temperature in the room or disconnect a particular room from the system if it is not needed.
- When installing the system, pipes of small diameter are taken.
- The tightness of the system eliminates the appearance air jams in radiators.

Among the disadvantages is the fact that the system will not be able to function without electricity. If the power supply is turned off, the pump will stop working.
The only solution to the problem of power outages may be to install an autonomous generator, but this is an additional source of expense.
If not correct installation pipes of the system, which will cause disruption of its operation. Therefore, it is very important after installing all elements of the heating system to check it for leaks.
Closed heating system: single-pipe circuit
You can assemble a closed heating system with your own hands, having decided which scheme - one-pipe or two-pipe - will be used during installation.
The single-pipe heating system is closed and is considered optimal for small cottages.
All heating devices– radiators communicate with each other in turn. When installing the system, you need to use a powerful pump that will help the coolant quickly reach the end point of the system.

The expansion tank performs a number of important functions in the system. You can read about why it is needed and how to choose it correctly at
In this system it is not possible to install coolant return risers. During use, it is impossible to regulate the heat supply in certain rooms; if the temperature in one room decreases, the temperature throughout the house will decrease.
IN multi-storey buildings It is best to use a vertical single-pipe system, with the connection made from the highest point. It is not recommended to connect more than 10 heating devices along the riser. As a rule, the radiators on the 1st floor heat less efficiently than on the last.
What is a two-pipe closed heating system?
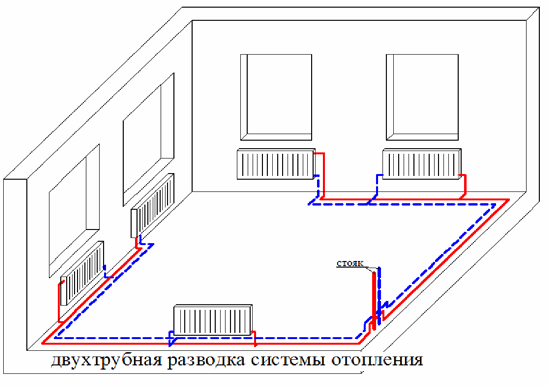
In a two-pipe closed-type heating system, the carrier (water, antifreeze) goes up the riser and is connected directly to a separate radiator. The heating system is characterized by high performance - water is distributed through the radiators at the same temperature, then goes down the riser back into the heating boiler.
For a private house, a two-pipe horizontal heating system is used.
With this heating scheme, you can regulate the flow and temperature on each radiator by installing a thermostat on the battery. All other batteries will not be affected by disconnecting one cell. Experts recommend installing for each radiator it is necessary to install for forcing excess air when starting the system before the heating season.
In a two-pipe closed-type heating system, there is no need to install a hydraulic pump - the coolant distributes through the pipes independently.
When choosing between two heating schemes, you need to take into account that for all the efficiency of the two-pipe scheme, it requires 2 times more materials– pipes and fasteners.
Types of a closed heating system for a private house (video)
A closed-type heating system has many advantages, hence its popularity. With proper installation of the system elements and subsequent operation of the heating, the owner will not need to interfere with the work for a long time. It is important to periodically clean the expansion tank and air vent to avoid malfunctions.
A water heating system that uses a membrane expansion tank and the coolant is in no way in contact with atmospheric air is considered closed and operates under pressure. This scheme is the most common at the moment because it has many advantages. In this article we will look at what a closed heating system in a private home is, its pros and cons, as well as maintenance features.
What is a closed heating system?
An important feature of such a system is the lack of contact with outside air and the presence of a small overpressure. As a rule, the scheme works by artificially stimulating coolant circulation using a pump. This allows you not to worry about maintaining large slopes of pipelines, as well as accepting smaller pipe diameters and laying them in the most convenient way.
As a rule, a gravity heating system with natural circulation of coolant is made with an open expansion tank installed at the highest point. A closed system is traditionally equipped with a circulation pump, which increases its operating efficiency and reduces material consumption.
Due to their features, closed-type systems have many advantages:
- coolant under pressure heats up faster;
- the likelihood of airing the network of pipelines and radiators is very low;
- the coolant is not saturated with oxygen and does not evaporate into the atmosphere, which is very important when filling the system with antifreeze;
- installation of an expansion tank in a closed heating system is carried out on the return pipeline near the boiler, which is very convenient in terms of maintenance;
- there is no need to use large diameter pipelines and lay them in plain sight; in this regard, a closed system with forced circulation is optimal choice for a private home.
There is only one significant drawback - dependence on the reliability of the power supply; a closed heating system without a pump powered from the mains will not work. Fortunately, circulation units for individual systems have low power consumption, and therefore can operate from the unit during a power outage uninterruptible power supply for quite a long time.
Some experts argue that a closed system with natural circulation will help solve the problem of power outages. Let us recall that in this case the movement of the coolant occurs due to the difference in the density and mass of hot and cooled water. The first, heating up in the boiler, being lighter, is forced upward by the cooled coolant coming from the radiators, which has a large mass.
Despite the fact that the pressure in a closed heating system (1.5-2 Bar) does not prevent the gravitational movement of hot and cold water flows, the effectiveness of its operation is very doubtful. The fact is that the difference in convective forces is already small, but here you still need to overcome the resistance of the tank membrane, which stretches as the water expands. To avoid these slippery moments, it is better to always install a pump on a closed system. If there is a need to install a gravity circuit, then it must be made open.
Diagram of a closed heating system
In private housing construction, 2 types of schemes are traditionally used:
- single-pipe;
- two-pipe.

Single-pipe, better known as “Leningradka”, works satisfactorily in one - and two-story houses small area, when no more than 5 radiators are installed on each floor. The implementation of the scheme requires an accurate calculation of the diameters of the pipes and the number of battery sections, since the coolant cools down significantly after passing through each subsequent radiator. A single-pipe diagram of a closed-type heating system with top wiring, as shown in the figure below, also requires compliance with these requirements:

Note. Regardless of the type of circuit chosen, the closed system must contain a safety group; sometimes it comes complete with the boiler. The group consists of a pressure gauge for pressure control, an air vent and a safety valve for emergency water release. The unit is installed on the supply pipeline leaving the boiler, without any shut-off valves.
The two-pipe scheme of a closed system is easier to calculate and install, and is famous for its popularity due to its good performance indicators. After all, the coolant is delivered to all radiators at the same temperature, and when implementing a passing scheme, it also travels the same distance. Example two-pipe system shown in the picture:

Some extras include a closed heating system with solid fuel boiler. To avoid the formation of condensation in the heat generator furnace, the circuit is supplemented mixing unit With three way valve and bypass line. The valve causes water to circulate through the bypass until it heats up to set temperature, and only then releases coolant from the main into the boiler.

How to fill the system with coolant?
When the make-up connection is connected to water supply network through ball valve, then filling a closed-type heating system with coolant is quite simple. For this task, it makes sense to hire an assistant, especially if the house has several floors. One person operates the charging valve, and the second is engaged in releasing air from the batteries. The tap opens about a third so that the pressure is not strong.

A person in the boiler room monitors the readings of the pressure gauge; the replenishment of the closed heating system is closed when the pressure reaches 2 Bar. Now the assistant uses Mayevsky’s taps to bleed air from the radiators, after which the pressure drops. The goal is to reach the design pressure by removing all the air from the pipelines by gradually displacing it with tap water.

It is more difficult to pump coolant into a closed system when there is no make-up from the water supply or you need to fill in an antifreeze liquid. To do this, you will need a special manual or electric pump and a container for the coolant from which it will be pumped into the system. First you need to open all the air valves on the radiators, and then fill the pipes through the drain fitting by connecting a pump with a check valve to it.

As the liquid is pumped in, it is necessary to close the Mayevsky taps, from which the coolant will flow. Having pumped the system to 1.5 Bar, it is necessary to remove air, after which the pressure is brought to working pressure. At the end it is produced trial run boiler and adjusting the pressure, and, if necessary, bleeding air.
Why does pressure drop in a closed heating system?
There is only one reason why pressure drops - lack of tightness, that is, leakage. The question is to find it. A characteristic feature a leak is a puddle in a certain place or brown spot when the water has time to dry. During the search process, you should inspect the following nodes and elements:
- pipe connections and fittings: it happens that cracks appear in the latter;
- automatic air vents: faulty element with a stuck float it will leak water;
- shut-off and control valves, safety valve;
- expansion tank: a crack in the membrane will cause a drop in pressure, the appearance of air in the system and frequent shutdowns of the boiler.
To eliminate a leak, it is impossible to do without partially or completely emptying the pipelines. Upon completion of the work, you will have to refill the system with water, create the necessary pressure and monitor the pressure gauge for several days.
Conclusion
A closed heating system has many advantages, hence its popularity. If installation and commissioning are carried out correctly, then it does not require intervention in its operation for a long time. Most of the problems that arise can be easily fixed with your own hands, as well as system maintenance. It is advisable to annually check the performance of elements such as air vents, valves and expansion tank.
Water heating in an individual residential building consists of a boiler and radiators connected by pipes. The water is heated in the boiler, moves through pipes to the radiators, gives off heat in the radiators and again enters the boiler.
Central heating is arranged in the same way as autonomous heating. The difference is that a central boiler house or CHP heats many houses.
The terms “closed system” and “open system” are used to characterize autonomous heating and central heating, but differ in meaning:
- In autonomous heating systems open systems are those that communicate with the atmosphere through an expansion vessel. Systems that have no communication with the atmosphere are called closed.
- In houses with central heating, an open system is called, where hot water to the taps comes directly from the heating system. And closed, when the hot water entering the house heats the tap water in the heat exchanger.
Autonomous heating systems
The water that fills the boiler, pipes and radiators expands when heated. The pressure inside rises sharply. If you do not provide for the possibility of removing the additional volume of water, the system will rupture. Compensation for changes in water volumes when temperature changes occurs in expansion vessels. As the temperature rises, excess water moves into the expansion vessel. As the temperature decreases, the system is replenished with water from the expansion vessel.
- Open system permanently connected to the atmosphere through an open expansion vessel. The vessel is made in the form of a rectangular or round tank. The form doesn't matter. It is important that it has sufficient capacity to accommodate the additional volume of water generated from thermal expansion circulating water. The expansion vessel is located in the highest part of the heating system. The vessel is connected to the heating system by a pipe called a riser. The riser is attached at the bottom of the tank - to the bottom or side wall. A drain pipe is connected to the top of the expansion tank. It is discharged into the sewer or outside the building. A drain pipe needed in case the tank overfills. It also ensures a constant connection between the tank and the heating system and the atmosphere. If the system is filled with water manually using buckets, the tank is additionally equipped with a lid or hatch. If the tank capacity is selected correctly, the water level in the tank is checked before turning on the heating. The water pressure in an “open system” is equal to atmospheric pressure, and does not change when the temperature of the water that circulates in the system changes. No overpressure safety device is required.
- Closed system isolated from the atmosphere. The expansion vessel is sealed. The shape of the vessel is chosen so that it can withstand the greatest pressure at minimum thickness walls Inside the vessel there is a rubber membrane that divides it into two parts. One part is filled with air, the other part is connected to the heating system. The expansion vessel can be installed at any point in the system. As the water temperature increases, the excess enters the expansion vessel. The air or gas in the other half of the membrane is compressed. As the temperature decreases, the pressure in the system decreases, the water from the expansion vessel is under the influence compressed air is forced out of the expansion vessel into the system. In a closed system, the pressure is higher than in an open system and constantly changes depending on the temperature of the circulating water. In addition, a closed system must be equipped safety valve in case of a dangerous increase in pressure and a device for releasing air.

District heating
Water at central heating heated in a central boiler room or thermal power plant. This is where the expansion of water with temperature changes is compensated. Next, hot water is pumped into the heating network. Houses are connected to the heating network by two pipelines - direct and return. Having entered the house through a direct pipeline, the water is divided in two directions - for heating and for hot water supply.
- Open system. The water is coming directly to the taps hot water, and is discharged into the sewer after use. An “open system” is simpler than a closed one, but in central boiler houses and thermal power plants it is necessary to perform additional water treatment - purification and air removal. For residents, this water is more expensive than tap water, and its quality is lower.
- Closed system. Water passes through the boiler, giving off heat for heating tap water, connects to the heating return water and returns to the heating network. Heated tap water flows into hot water taps. A closed system, due to the use of heat exchangers, is more difficult than an open one, but tap water is not exposed to additional processing, but only heats up.

To ensure heating of a two-story building or home with quite large area It is better not to use a heating system with natural circulation. Since the coolant in this system moves extremely slowly, it will be very difficult to quickly warm up the room. You can avoid this problem if you initially choose a closed heating system with forced circulation.
Forced movement of coolant
The forced heating scheme is distinguished from natural heating by the presence of a circulation pump. With its help, the coolant moves through the main pipeline at the speed required technical specifications, and not due to temperature differences. The pump creates the pressure necessary for the movement of heated water, but at the same time ensuring proportional distribution of the coolant heated to the required temperature.
The heating system of a private house with forced circulation includes:

When choosing the equipment necessary to operate the system, you need to take into account mandatory parameters such as the performance of the boiler and heating elements, the dimensions of the pipeline, the speed of movement of the heated working fluid. Heating system circuits can be designed with either single-pipe or two-pipe wiring.


Closed heating system
The main feature of a closed heating system, which distinguishes it from an open one, is the lack of contact with the external environment. In such a scheme, a circulation pump is necessarily provided for forced circulation of the heated working fluid. Thermal expansion leveled using a membrane-type expansion tank filled with liquid when heated. When cooled, the liquid from the reservoir re-enters the system, thus maintaining stable pressure in the heating line.

 The disadvantage of this system is energy dependence, but at uninterrupted power supply the closed system operates at full capacity. The circuit is relatively easy to install, and it can be implemented in rooms with any square footage.
The disadvantage of this system is energy dependence, but at uninterrupted power supply the closed system operates at full capacity. The circuit is relatively easy to install, and it can be implemented in rooms with any square footage.
The pipeline does not require insulation; heating is carried out almost instantly. The presence of a thermostat allows you to regulate temperature regime and create a suitable microclimate in the home. TO undeniable advantages closed-type heat supply systems can be attributed to the fact that the temperature difference between the supply and return pipelines makes it possible to increase the service life of boiler equipment, and the closed circuit protects the pipeline from corrosion. If there is a need for a long period turn off the heating, then to preserve the pipeline, it makes sense to fill it with antifreeze.
2. Main elements of a forced circulation heating system
Forced heating circuit. Forced circulation heating circuit


Air lock protection
Hypothetically, there should be no air in a closed heating circuit, but in reality a small amount of it is still contained. Air may accumulate as the system fills with water. Another reason for airing may be loss of tightness in butt joints. As a result, the productivity level of the system decreases.
To effectively counteract this phenomenon, special air bleed fittings are used. To minimize the possibility of air accumulation, certain rules must be followed:

For aluminum radiators the presence of air vents is mandatory, since aluminum, interacting with water, leads to chemical reaction accompanied by the release of oxygen.
WITH bimetallic radiators The same difficulties arise, but the air accumulates in them in a smaller volume.
LENINGRAD! The most reliable system heating


Single-pipe wiring diagram
A single-pipe heat supply system involves a combination of supply and return lines. The heated liquid is directed through a special pipeline with fittings designed to block the flow of coolant. The design also provides for a separate pipe with a tap for discharging water into the drainage.

 After the liquid in the boiler is heated, it passes through the risers and heating devices and, sharing with them required quantity heat ends up in the pump. To prevent an emergency, a membrane expansion tank of a closed (closed) or open type is used.
After the liquid in the boiler is heated, it passes through the risers and heating devices and, sharing with them required quantity heat ends up in the pump. To prevent an emergency, a membrane expansion tank of a closed (closed) or open type is used.
Its installation is carried out on technical floor premises (highest point). By design features The expansion tank also characterizes the heating system itself. That is, if the tank is closed, then the heating system will be closed.
In a one-pipe system it is necessary to include a security group that contains:
- air vent;
- safety valve;
- pressure gauge and thermometer, often integrated in one device.
This group allows you to effectively reduce the level of excess pressure, thereby preventing water hammer and equipment failure. It would also be advisable to take into account the connection of thermostats and Mayevsky taps to each heating element.
The connection of heating devices in this scheme can be diagonal, parallel, and so on. A single-pipe heating circuit allows design with vertical or horizontal wiring. Both methods make it possible to connect to a water heating device or warm floor. To implement such a project, it is necessary to have a distribution manifold that allows the heated coolant to be delivered directly to the boiler, heating devices and heated floors.
Supply and return lines
A distinctive feature of this project is the presence of two heating circuits. One circuit transports and distributes the working fluid heated in the boiler to the heating elements. Through the second circuit, the cooled coolant is returned back to the boiler unit. The design of the two-pipe circuit makes possible to carry out repair work individual heating units without shutting off the heat supply. Installing thermostats on each battery allows you to adjust heat consumption and minimize costs.

 This system ensures uniform heating of each section of the battery. Two-pipe piping allows you to avoid significant pressure losses, which, in turn, eliminates the need to purchase a powerful circulation pump. One more additional benefit In a two-pipe main, it is considered possible to use dead-end and associated movement of the coolant. In the associated scheme, the movement of the coolant in the supply and return lines is carried out along the same vector.
This system ensures uniform heating of each section of the battery. Two-pipe piping allows you to avoid significant pressure losses, which, in turn, eliminates the need to purchase a powerful circulation pump. One more additional benefit In a two-pipe main, it is considered possible to use dead-end and associated movement of the coolant. In the associated scheme, the movement of the coolant in the supply and return lines is carried out along the same vector.
With this movement it is created perfect hydraulic balance, considering that the power of the radiators used is the same. Therefore, there is no need additional use battery presetting valves. Associated scheme movement is used in long-distance main pipelines. A dead-end circuit is usually used for heating residential buildings. At the end installation work the system is being pressurized.
