Installation of tongue-and-groove slabs is carried out using technology that is used in Lately professional builders and home craftsmen increasingly. These products have low weight, reliable locking connections and convenient sizes. All this allows you to install them without much effort, remodeling the premises as required by personal preferences.
Types and features of tongue-and-groove products
Before you begin installing tongue-and-groove slabs, you need to understand what types of these products are on the market today. They are silicate and gypsum, the latter are made from the material of the same name, to which a plasticizing admixture is added. For the production of silicate sand, lump and quartz sand are used, which are pressed and kept in an autoclave.
Which slabs to choose
If you want to give your walls heat-insulating qualities, it is better to prefer gypsum boards; they do not allow sound to pass through. However, silicate ones are able to withstand higher mechanical loads and also absorb less moisture. Tongue-and-groove slabs, which can be easily installed with your own hands, are environmentally friendly, so they can be used for furnishing residential premises. The materials are not flammable, do not rot, do not emit harmful substances into the atmosphere and are not deformed. On sale you can find solid ones that can reduce the weight of masonry by 25%. If we talk about the dimensions of the gypsum boards, they are 500 x 667 x 80 mm. But silicate ones are more compact: 250 x 500 x 70 mm. Once you have dealt with all the supporting structures, you can begin laying tongue-and-groove products, but this must be done before installation finishing coating on the floor and holding finishing works.

Preparation of tools and materials
Installation of tongue-and-groove slabs is carried out after preparing a certain set of tools and materials. These products can be installed in the center of the room, as well as against a wall that goes outside the building or into a cold room. By forming double partitions, you can hide wiring, other systems and communications.
To divide a room into separate zones, you can use partitions, the height of which starts from 80 cm. For installation you will need:
- building level;
- adhesive composition;
- anchor dowels;
- gypsum mortar;
- putty knife;
- screwdriver;
- cement-sand mortar;
- Staples;
- felt seal;
- primer;
- hacksaw;
- rubber mallet.

Preparing the site
Installation of tongue-and-groove slabs begins with site preparation. To do this, you should check the evenness of the walls and floor where the products will fit. If there are defects such as sagging, then they should be removed by grinding. The walls and floor should also be freed from cracks and depressions, filling the errors with a cement-sand mixture.
As soon as the bases are dry, they should be coated with a primer. If you decide to install a partition during the process of ongoing repairs, then the contact lines should be marked on the floor and walls. After finishing coat cut along the markings so that the base can be seen. For paint, wallpaper, decorative plaster You cannot install slabs; this applies to laminate, parquet and linoleum. If the surfaces have a decorative coating in the form of ceramic tiles, then they do not need to be removed, but the surface is first checked for strength.
The tongue-and-groove slab must be installed correctly; to do this, a cord should be pulled between the walls over the entire area, moving it 30 cm from the floor surface. This will allow you to control the vertical placement of the products. Along the contact line it is necessary to stick a sealant, the width of which must correspond to the thickness of the slab. In the role of this material You can use bitumen-impregnated felt or a cork backing.

Working on the first row
Installation of a tongue-and-groove slab cannot be called difficult work, however, it is necessary to approach this issue extremely carefully. To install the starting row of slabs, it is necessary to cut off the lower ridges using a hacksaw. Glue is applied to the seal, which must be on a vertical and horizontal surface. The first slab is installed on the side where it will adjoin the wall. The perforated bracket is inserted into the groove. The bracket should protrude a few centimeters above the slab. It is fixed to the wall with self-tapping screws, or this is true when you are working on a concrete base.
The slab should be facing upward with the groove, it is leveled and pressed against the base, tapping it with a mallet. In the place where the second slab will adjoin, it is necessary to install a piece of bracket and secure it with dowels to the floor. If it turns out that this product is installed unevenly, then the rest will repeat the angle of inclination. In this situation, it will not be possible to level the masonry; the interlocking connections will interfere. This explains the need to level the first slab of the bottom row. The composition is applied to the side grooves and ridges so that the seams between the plates are not thicker than 2 mm. Excess mixture should be removed with a spatula, checking the masonry building level. A bracket is installed in the lower part and fixed to the floor with anchor dowels. Each subsequent product must be installed after setting adhesive composition on the previous one.

Installation of the following rows
Installation of walls made of tongue-and-groove slabs involves displacement of the seams in the second and subsequent rows. To ensure this condition, the slab must be cut in half. At the end and beginning of the row, staples should be fixed on the cuts. This must be done in the place where the sections adjoin the wall. The glue should be more liquid; it should be applied to the bottom and side grooves of each product. It is important at this stage to check the vertical and horizontal of the masonry. The next row is installed only after the glue has set in the second row.

Formation of the last row
Usually not accompanied by difficulties. However, it is important to pay special attention to the entire process. For example, the top row should not be adjacent to the ceiling. Approximately 1.5 cm should be left between the plates and the horizontal surface. To do this, staples are installed in the upper grooves of the final row using glue and screwed to the ceiling with dowels. After installation is complete, the gap can be filled with foam, the excess of which is cut off after hardening.
Features of installation of Knauf brand slabs
Knauf tongue-and-groove slabs, the installation of which requires compliance with certain nuances, can be installed by a home craftsman independently. For example, when preparing, it is important to ensure that the subfloor where work will be carried out is stationary, level and stable. If there are unevennesses that exceed more than 10 mm, then it is necessary to form a leveling layer; this can only be done under the partition.
Before starting manipulations, the surface is cleaned of dirt and construction waste, as well as oil stains. To prepare the mixture, pour the dry composition into a clean plastic container with water. The liquid should be at room temperature. The composition is mixed using a drill with an attachment or an electric mixer. The solution is left for a few minutes and then mixed again. It is recommended to cook it in portions, one of which you can finish in the next half hour.
Such a tongue-and-groove gypsum board, which is often installed independently, can be installed in one of two ways. The first involves the use of glue, which is applied to concrete base. This method allows you to obtain a rigid mount. The composition is applied to the floor and walls in an even layer, and the average consumption for an 80 mm slab will be approximately 2 kg per square meter. If the thickness of the partition increases to 100 mm, then the glue consumption will be equal to 2.5 kg.
The second method involves fastening to walls, ceilings and floors through an elastic cork gasket. This method allows for higher sound insulation, especially for impact noise such as door slams and knocking. Such products are laid with the ridge or groove up. It is more practical to install it on top with a groove, since in this case it is more convenient to lay the glue than to try to spread it on the ridge. If the ridge is located on top, then it should be removed using a hacksaw with large teeth. Sometimes elements are removed using a roughing plane until a smooth surface is achieved.

Features of installation of tongue-and-groove slabs of the Volma brand
The Volma tongue-and-groove slab, which is installed using the same technology as described above, is a product with a total area of 0.33 m2. The plate is made from hydrophobic and plasticizing additives, which are complemented by lithium technology during the manufacturing process. The products are intended for the formation of partitions in rooms and buildings for various purposes with a normal and dry microclimate.
You can control the resulting plane by applying a rule or a regular strip to the wall at different angles. If necessary, the plane can be adjusted until the glue sets. It is important to ensure that the slabs are glued together at four ends. Any excess compound that appears must be rubbed down with a spatula before sealing the seam. You should not begin laying the second row until you have measured the remaining gap for which the section is being prepared. The additional element will become the beginning of a new row. This will allow the vertical seams to spread apart.
You will be able to install tongue-and-groove slabs with your own hands; the tips presented in the article will help you with this. From them you can learn that the slabs must be laid down from the sides and from above; they must be used for this only so as not to damage the blocks. This rule should not be neglected, since otherwise it will not be possible to achieve a tight connection between the tongue and groove.
Adhesive for tongue-and-groove slabs "Fugen"
If you decide to purchase glue for installing tongue-and-groove slabs, then you can pay attention to the “Fugen” mixture, which is offered by the Knauf company. It should take approximately 1.5 kg per square meter. If joints between sheets of drywall are sealed, the consumption will be 0.25 kg. This mixture is a dry composition, which is made on the basis of gypsum and polymer additives.
The solution is intended for sealing seams and cracks. To prepare, the dry mixture is poured into a container with cold water. For 1.9 liters of water you will need 2.5 kg of composition. After evenly distributing the dry mixture, it is necessary to hold it for 3 minutes and mix until a homogeneous mass is obtained. Its consistency should resemble thick sour cream.
Conclusion
If, when laying a partition, you plan to make a window or doorway, then you need to think about the technology for attaching the slabs above it. If the opening has a width not exceeding 80 cm, then the product can be installed on a box or temporary support. This is true provided that there is one row of blocks per opening. If the width is greater specified value or there will be several rows, then it is necessary to form a strong jumper.
Tongue-and-groove slabs are rectangular gypsum parallelepipeds intended for the installation of internal load-bearing partitions in rooms with varying degrees of humidity. There are hollow and solid versions of their execution.
KNAUF tongue-and-groove slabs
One of the most famous manufacturers gypsum board is produced by the German concern KNAUF. The brand's products are available in three sizes: 667x500x80, 667x500x100 and 900x300x80.
Material of tongue-and-groove slabs
The basis for the production of KNAUF tongue-and-groove slabs is gypsum binder of two grades: G-4 or G-5. The material does not support combustion and does not contain toxic components, which allows its use in hospitals and kindergartens. He doesn't spend electricity and is resistant to sudden changes in temperature. A high degree of vapor permeability is characteristic of all gypsum products. The material lends itself perfectly machining and has no specific odor.
installation of partitions from tongue-and-groove slabs. Photo
Technical description of KNAUF boards
The KNAUF tongue-and-groove plate has the form of a rectangular parallelepiped, the design of which provides for a special high-precision tongue-and-groove connection. Ready product has the following technical characteristics for all sizes:

Installation of partitions using KNAUF slabs
Do-it-yourself partition made of tongue-and-groove slabs. Video instruction
Partitions made from KNAUF tongue-and-groove slabs are constructed using the designer method, by precisely connecting a groove on the supporting side and a tongue on the joining side, with gluing of the joining surfaces. The adhesive mixture can be used as glue for gluing drywall " Pearlfix", produced by the KNAUF concern. Installation of tongue-and-groove slabs is carried out with precise adherence to rows in vertical as well as horizontal planes.
Work on the construction of partitions should be carried out after the completion of the production of load-bearing elements of the room, but before laying the finishing floors. This period coincides with finishing work indoors, mainly during the cold season. Temperature indoors should not be below +5 °C. Humidity should correspond to dry or normal conditions. Before use, the slabs must undergo acclimatization, that is, adapt to indoor conditions. To do this, they must lie inside for at least 4 hours.
The permissible length of the partition is 6 m, and the height is 3.6 m. If it is necessary to erect a longer or higher partition, it is made up of separate fragments, each of which has a separate attachment to the supporting structures using a special frame.
Volma tongue-and-groove slabs (solid)
Volma solid slabs - have the shape rectangular parallelepipeds with a tongue-and-groove system, manufactured using injection molding technology. The main purpose is the construction of internal partitions in rooms with three types of humidity according to SNiP II-3-79. Moisture-resistant boards contain hydrophobic additives and special plasticizers. The moisture-resistant version has a characteristic green color.
The material of the stove does not support combustion and does not contain substances harmful to the human body. They have high sound insulation and do not have a specific odor. 
installation of walls made of Volma tongue-and-groove slabs. Photo
Technical characteristics of Volma slabs
The surface of the slab and the geometric accuracy of the design exclude plastering work when decorating a room. The solid slab is produced in one standard size - 667x500x80. The weight of one plate is 28 kg.
Volma tongue-and-groove slabs (hollow)
For the construction of partitions that require reducing the load on the base of the floor, Volma hollow plasterboards are provided. Their main application is the installation of interior structures in modern panel houses. This is due to the maximum load that the floor slabs can withstand. Like their solid counterparts, the slabs can be standard and moisture-resistant. The standard size remains the same: 667X500X80 mm. Often a hollow slab is used for cladding the outside of a room. The weight of a standard hollow slab is 20 kg, moisture resistant - 22 kg. Material properties hollow slabs similar to their full-bodied counterpart. 
Installation of partitions from Volma slabs
Installation of a partition made of Volma tongue-and-groove slabs is carried out by precise alignment of grooves and ridges on parallelepipeds, followed by gluing them. As glue mixture for Volma tongue-and-groove slabs, any adhesive for gluing drywall is used, including that recommended by the manufacturer “ Volma-montage" Installation of the partition structure is carried out in the following order:
Partition made of Volma tongue-and-groove slabs. Video instruction


Electrical installation in tongue-and-groove slabs
Electrical wiring in tongue-and-groove slabs is carried out by laying wires in pre-made grooves. The depth of laying the grooves has a limitation: it should not exceed 40 mm for a slab thickness of 80 mm, and 50 mm for a slab width of 100 mm. The wires are secured using alabaster or drywall glue. The landing sockets for undercutters should also not exceed the specified depth. Their arrangement is possible in a mirror image on both sides of the partition in through hole. But in this way the noise-absorbing properties of the structure are lost. For additional insulation of electrical wiring in tongue-and-groove slabs, corrugated tubes are used.

technology for installing tongue-and-groove slabs. Photo
Finishing walls from tongue-and-groove slabs
Like any other building surface, partitions made from tongue-and-groove slabs require all types of construction and finishing work. The advantage of such a partition is the absence of additional putty manipulations preceding decorative work. The finishing of a tongue-and-groove partition includes: painting the surface, laying ceramic tiles and natural stone, and wallpapering.
Laying ceramic tiles on tongue-and-groove walls
The process of laying ceramic tiles on plasterboard is similar to gluing tiles to drywall:

Due to the moisture-absorbing properties of gypsum, the finished surface should not be disturbed for three days.
Wallpapering walls made of tongue-and-groove slabs
Before gluing the wallpaper to the tongue-and-groove partition, you should make small finishing Painting works . This could be the application of a thin layer of ready-made plaster, for example, “ Rotband" Or covering the surface with a layer of finishing fine-grained putty. Before applying putty, the surface is treated with a primer deep penetration. After the putty has dried, the surface is ready for wallpapering. It is not necessary to treat the base with soil. Gluing wallpaper to partitions made of tongue-and-groove slabs is carried out according to the standard procedure, with glue applied both to the wallpaper and to the base of the surface being glued.

Painting walls made of tongue-and-groove slabs
The tongue-and-groove slab is also painted after finishing surfaces fine-grained putty. After the finishing layer has dried, it is carefully rubbed with a fine sanding mesh under the light of a construction lamp. This is necessary to avoid irregularities and roughness invisible to the eye. The surface to be painted should be treated with a primer and given time to dry. After this, you can apply one or more layers of paint as needed.
Before any type of finishing of the tongue-and-groove partition, it must be thoroughly cleaned and treated with a primer.
Do-it-yourself installation of tongue-and-groove slabs. Video
T technological map for the installation of partitions
from tongue-and-groove slabs
Routing
(TTK)
Explanatory note
2012
1 area of use
The technological map has been developed for the installation of partitions from tongue-and-groove slabs in buildings and structures for various purposes.
The material for the manufacture of tongue-and-groove slabs is gypsum. The surface of partitions made of gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs is suitable for any finishing and does not require the application of a leveling plaster layer. Application of lime paints and paints based on liquid glass is not allowed.
When linking a technological map to a specific object and construction conditions, the following is specified:
Scope of work performed;
Work schedule and duration;
Quantitative composition of units and means of mechanization.
The technological map has been developed in accordance with current Russian and departmental documents:
Table 1
Permissible deviations of partitions made of tongue-and-groove slabs
|
Permissible deviations during finishing |
|||
|
simple |
improved |
high quality |
|
|
Surface irregularities (detected when applying a rule or template 2 m long) |
No more than 3 mm in depth or convexity up to 5 mm |
No more than 2 mm deep or convex up to 3 mm |
No more than 2 mm deep or convex up to 2 mm |
|
Vertical surface deviation |
15 mm for the entire height of the room |
1 mm per 1 m height, but not more than 10 mm over the entire height of the room |
1 mm per 1 m height, but not more than 6 mm over the entire height of the room |
5. Need for material and technical resources
The need for machines, mechanisms, tools and devices for installing partitions from tongue-and-groove slabs is determined taking into account the volume of work performed, purpose and technical characteristics according to the table.
table 2
List of requirements for machines, mechanisms, tools and devices
|
Name |
Type, brand, GOST |
Purpose |
||||
|
Cord breaker device |
||||||
|
Device "Metrostat" |
||||||
|
Masonry control |
||||||
|
Masonry control |
||||||
|
Rubber hammer |
Installing the slab in the design position |
|||||
|
For storing the solution |
||||||
|
Putty knife ( different kinds) |
Application adhesive solution, leveling the surface of the partition |
|||||
|
Hand sander |
Surface grinding |
|||||
|
Slab adjustment |
||||||
|
Roughing plane |
||||||
|
Furrowmaker |
Strobe device |
|||||
|
Electric drill |
||||||
|
Attachment for an electric drill for making large-diameter holes |
||||||
|
Metal scissors |
Installation management is entrusted to experienced engineering and technical workers who are responsible for the safe organization of installation work. Cranes, lifting mechanisms and auxiliary devices used during installation work must meet the established requirements of the inspection rules of Gosgortekhnadzor. Before starting installation work and periodically during work, all used rigging and installation devices (slings, crossbeams, etc.) must be surveyed and inspected in accordance with the Rules for the Design and Safe Operation of Load-Lifting Cranes. Workers at least 18 years of age who have completed training are allowed to carry out installation work. medical checkup and safety training and appropriate certifications. Installers, welders and other workers involved in the installation of the main structures of the house must be provided with proven safety belts. In the area (occupancy) where installation work is being carried out, other work and the presence of unauthorized persons are not allowed. During breaks in work, it is not allowed to leave raised structural elements hanging. Unslinging parts during unloading or loading is allowed only after checking their stability. On floors, scaffolding and scaffolding, only assembly, installation and fitting are allowed. Work on the production of missing parts on scaffolding and scaffolding is not allowed. Before performing installation work, it is necessary to establish a procedure for the exchange of conditioned signals between the person supervising the installation and the driver (motor operator). All signals are given by only one person (the foreman of the installation team, the team leader, the rigger-slinger), except for the “Stop” signal, which can be given by any worker who notices an obvious danger. Installation of structures of each subsequent tier (section) of a building or structure should be carried out only after all elements of the previous tier (section) have been securely fastened according to the project. Hanging metal stairs with a height of more than 5 m must be fenced with metal arches with vertical connections and securely attached to the structure or equipment. Climbing workers on hanging ladders to a height of more than 10 m is permitted if the ladders are equipped with rest areas at least every 10 m in height. 7. Technical and economic indicatorsThe composition of the link for installing partitions from tongue-and-groove slabs is given in the table Bricklayer |
The costs of labor and machine time for installing partitions are calculated according to the “Unified Standards and Prices for Construction, Installation and Repair Work”, put into effect in 1987; collection E1 “In-building transport work”, collection E3 “Stone work” and are presented in the table.
To calculate labor costs and machine time, gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs with dimensions of 667×500×100 were used.
The calculation provides for the supply of two-thirds of the blocks and mortar using a jib crane from the ceiling to workplace. The supply of materials by lift to the floors is not taken into account in this map.
Table 4
Calculation of labor costs and machine time for the installation of partitions
|
Justification (ENiR and other standards) |
Scope of work |
Standard time |
Labor costs |
|||||
|
workers, person-hours |
workers, person-hours |
driver, person-hour (machine operation, machine hours) |
||||||
|
Transportation of slabs by hand trucks |
||||||||
|
Transportation of solution by hand trucks |
||||||||
|
Transportation of slabs |
||||||||
|
Transporting the solution onto the scaffolding |
||||||||
|
Installation of partitions |
||||||||
Duration of work on installing partitions using wall blocks made of cellular concrete determined calendar plan production of work according to the table.
Main technical and economic indicators
Scope of work:
Partitions made of foam concrete blocks made of cellular concrete 100 m 2
Labor costs for the entire scope of work, man-hour 59.72
Output per worker per shift, m 2 12
Table 5
Schedule of work for installing partitions

Prepared by NGO specialistsAbout "Construction Technologies"
This Code of Rules contains instructions on constructive solutions for partitions and wall claddings using gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs and methods of their installation, the implementation of which ensures compliance with the mandatory requirements for such structures established by current regulatory documents.
The choice of a specific design solution and materials for constructing structures falls within the competence of the design or construction organization.
If the decisions and materials recommended in this document are adopted for implementation, all rules established herein must be complied with in full.
The document was developed taking into account the experience of constructing these structures from materials supplied by KNAUF group enterprises. If materials from other manufacturers are used for the construction of structures provided for in this Code of Practice, their compliance with the requirements of this document must be confirmed in the prescribed manner.
The set of rules is intended for design and construction organizations, as well as operational services.
The set of rules was developed by TsNIIPromzdaniy OJSC (Deputy General Director, Candidate of Technical Sciences, Honored Builder of the Russian Federation CM. Glikin), LLC "KNAUF MARKETING NOVOMOSKOVSK" ( CEO I.E. Kovaleva) and KNAUF SERVICE LLC (consulting engineer T.N. Skvortsov).
SP 55-103-2004
CODE OF RULES FOR DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION
DESIGNS WITH APPLICATION
Gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs
STRUCTURES WITH APPLICATION
GYPSUM PLATES
Date of introduction 2004-10-01
1 AREA OF USE
Structures using gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs can be used in buildings for various purposes, with varying degrees of fire resistance and functional class fire danger, any number of storeys and any structural systems erected in all climatic regions of the country, including seismic regions and areas with other special conditions, while meeting the regulatory requirements for structures.
2 REGULATORY REFERENCES
The list of regulatory documents referenced in this Code of Practice is given in the Appendix.
3 GENERAL PROVISIONS
3.1 This Code of Practice should be used to guide the design, construction and operation of enclosing structures using gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs in residential, public, administrative and industrial buildings.
3.2 This Code of Rules contains recommended design solutions for partitions and wall cladding using gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs, as well as component materials and products supplied by KNAUF group enterprises, specified in section . When applying these technical solutions, the design parameters provided for in this Code of Practice, including cross-sectional dimensions, the maximum permissible height of structures, as well as the connection devicetions and interfaces with other building structures may be used directly without carrying out supporting calculations. If slabs and component materials and products are used that differ from those specified in the section , the above parameters must be determined by calculation or test results.
3.3 Products and materials specified in the section , must meet the requirements of the relevant standards or technical specifications, and for materials supplied abroad - a certificate of conformity (if there is a domestic analogue) or a technical certificate (if there is no domestic analogue).
3.4 Materials and products must have mandatory accompanying documentation, including: certificates of conformity (for materials subject to mandatory certification); hygienic conclusion (for materials included in the list approved by the Russian Ministry of Health); fire safety certificates (for materials included in the list of products subject to mandatory certification in the field of fire safety); instructions for use.
4 MATERIALS USED FOR CONSTRUCTIONS MADE FROM GYPSUM TONGUE BOARDS
4.1 Gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs
4.1.1 This Code of Rules for the construction of structures provides for the use of gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs in accordance with TU 5742-007-16415648-98, TU 5742-014-03984362-96, TU 5742-001-56798576-2004 and TU 5742-003-05287561-2003, physical - technical characteristics of which are given in the table .
4.1.2 The range of gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs includes ordinary and hydrophobized (moisture resistant) slabs, solid and PUhundred-bodied. Ordinary slabs should be used in enclosing structures of rooms with dry and normal humidity conditions, and hydrophobized ones can also be used in rooms with wet conditions according to SNiP 23-02.
Table 4.1
|
Index |
Unit change |
Plates according to specifications |
||||||
|
TU 5742-007-16415648-98 |
TU 5742-014-03984362-96 |
TU 5742-001-56798576-2004 |
TU 5742-003-05287561-2003 |
|||||
|
ordinary |
hydroph. |
|||||||
|
Density, no more |
kg/m 3 |
1250 |
1100 |
1200 |
||||
|
Holiday humidity, no more |
||||||||
|
Compressive strength, not less |
MPa |
|||||||
|
Bending strength, not less |
MPa |
|||||||
|
Coefficient of thermal conductivity: l A |
W/m × °C |
0,29 |
||||||
|
l B |
0,35 |
|||||||
|
Water absorption of hydrophobized slabs, no more |
||||||||
|
Specific effective activity of radionuclides, no more |
Bq/kg |
|||||||
|
Flammability group according to GOST 30244 |
ng |
|||||||
Table 4.2
|
Slab dimensions, mm |
Permissible maximum deviations, mm |
||||||
|
Length L |
Width IN |
Thickness t |
Length L |
Width IN |
Thickness t |
||
|
TU 5742-007-16415648-98 |
80; 100 |
± 2 |
|||||
|
TU 5742-014-03984362-96 |
|||||||
|
TU 5742-001-56798576-2004 |
80; 100 |
||||||
|
± 0,5 |
|||||||
|
TU 5742-003-05287561-2003 (solid) |
|||||||
|
± 5 |
|||||||
|
TU 5742-003-05287561-2003 (hollow) |
|||||||
|
Note - Plates according to TU 5742-007-16415648-98, TU 5742-014-03984362-96, TU 5742-001-56798576-2004 - solid. Plates according to TU 5742-003-05287561-2003 - hollow and solid. |
|||||||
In rooms with wet conditions, the use of gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs is not allowed.
4.1.3 The nominal dimensions of gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs and maximum deviations from the nominal dimensions are given in the table .
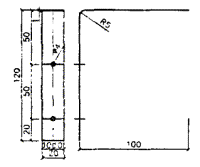
4.1.4 Gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs are shaped like a groove and a tongue various types(drawing ).
TU 5742-007-16415648-98
TU 5742-003-05287561-2003
TU 5742-014-03984362-96

TU 5742-001-56798576-2004

TU 5742-007-16415648-98
TU 5742-007-16415648-98
TU 5742-001-56798576-2004
Picture 1 - Types of gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs according to the shape of the groove and tongue (dimensions are given as a guide and are not a rejection criterion)
4.2 Accessories and products
4.2.1 For fastening partitions and cladding to enclosing structures with an elastic connection, as well as fastening door frames to partitions, it is recommended to use brackets, the nomenclature of which is given in the table .
4.2.2 To fasten brackets to tongue-and-groove plates, it is recommended to use self-tapping screws 35 mm long with countersunk head and a sharp end, made of steel grades 10, 10KP, 15, 15KP, 20 and 20KP according to GOST 10702 , and for attaching them to enclosing structures - expandable anchor dowels, the nomenclature of which is given in the table .
Table 4.3
|
Product and material designation |
Purpose |
|
|
|
Bracket S-1 For fastening partitions with elastic connection |
|
|
|
Bracket S-2 For fastening door frame to the partition |
|
|
|
Corner protection profile for finishing external corners of partitions |
Table 4.4
|
Name |
Length, mm |
Diameter, mm |
|
|
Self-tapping screw with a countersunk head and a sharp end (screw) |
|||
|
|
Plastic anchor dowel |
6 ,0 |
|
|
10,0 |
|||
|
|
Metal anchor dowel |
||
|
12,0 |
4.2.3 When elastically connecting partitions with other enclosing structures, it is recommended to use an elastic gasket made of cork with a density of at least 250 kg/m 3 or bituminized felt with a density of at least 300 kg/m 3 . The width of the spacers must be at least 75 mm for slabs 80 mm thick and at least 95 mm for slabs 100 mm thick.
4.2.4 When laying gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs, as well as for attaching elastic gaskets to enclosing structures, it is recommended to use glue from a dry putty mixture based on the gypsum binder “KNAUF-Fugen-Füller™” according to TU 5745-011-04001508-97 and TU 5745-021-03984362 -2001. When laying hydrophobized (moisture-resistant) gypsum boards, it is recommended to use the KNAUF-Fugenfüller Hydro™ putty mixture according to TU 5745-021-03984362-2001.
4.2.5 To protect internal corners in partitions and cladding made of gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs, reinforcing tape (serpyanka) should be used, and to protect external corners - procorner protective filler PU 31/31 according to TU 1121-004-04001508-2003 (table ).
4.2.6 To install a heat and sound insulating layer in partitions, the materials specified in the project documentation for a specific building.
4.2.7 To prepare the surface of partitions and cladding made of gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs for finishing, it is recommended to use the KNAUF-Tiefengrund™ primer supplied by the KNAUF group enterprises.
4.2.8 To prepare the surface of partitions and cladding made of gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs for high-quality painting, it is recommended to use the KNAUF-Finishpaste™ putty composition supplied by KNAUF group enterprises.
4.2.9 In rooms where the surfaces of structures made of gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs are exposed to direct moisture, they should be protected with KNAUF-Flechendicht™ waterproofing mastic, and in places where gypsum slab structures interface with each other and withFor floors, it is recommended to use a self-adhesive sealant waterproofing tape"KNAUF-Flechendichtband®", supplied by the KNAUF group of companies.
5 TECHNICAL SOLUTIONS FOR STRUCTURES FROM GYPSUM TONGUE BOARD PLATES
5.1 General provisions
5.1.1 This section applies to the design of structures of partitions and internal cladding of external walls made of gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs.
5.1.2 The section contains instructions on the design and design solutions of the main components of the structures listed above, their scope of application and physical and technical characteristics.
5.1.3 General requirements are imposed on structures using gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs in terms of:
Surface quality;
Fire-technical and hygienic characteristics of the materials used;
Characteristics of resistance to environmental influences, including high humidity and chemical aggression.
5.1.4 Meeting the requirements for surface quality, hygienic and fire-technical characteristics of structures is ensured by the properties of gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs, provided that they comply with the requirements of this Code of Rules.
5.1.5 Resistance of structures to influences environment provided under the following conditions:
For structures operating in humid temperature and humidity conditions, characterized by SNiP 23-02, hydrophobized gypsum boards are used;
For structures operating in aggressive environments, metal elements protected from corrosion in accordance with the requirements of SNiP 2.03.11.
5.2 Partitions
To the partitions building codes and the rules impose requirements in terms of resistance to the effects of its own weight, the weight of attached equipment, other operational, wind and seismic loads, as well as to the effects of accidental impacts.
Apartment partitions residential buildings(with the exception of interior partitions with openings) and partitions between work areas of non-production buildings must also meet sound insulation requirements.
Partitions separating heated and unheated premises buildings for various purposes must also meet the requirements for resistance to heat transfer and vapor barrier.
Partitions in buildings with standardized fire-technical characteristics of building structures must meet the requirements for the fire hazard class and fire resistance limit.
General requirements
5.2.1 This section applies to partitions used in rooms with dry, normal and wet conditions according to SNiP 23-02.
Table 5.1
|
Design |
Weight 1 m 2, kg |
|
|
|
Single |
100 |
|
|
Double |
200 |
|
|
Double with an additional layer of heat and sound insulating material |
200* 250* |
|
* Without taking into account the mass of the heat and sound insulating layer. Note - The numerator indicates the mass for partitions made of slabs with a thickness of 80 mm, and the denominator - 100 mm. |
||
5.2.3 When choosing partition schemes, force and other influences, the class of functional and structural hazards and the degree of fire resistance of the building, as well as space-planning parameters (including height) and operating conditions should be taken into account.
Design requirements
5.2.4 Partitions made of gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs should be designed from slabs of the same type as self-supporting structures and expect to be subject to the following loads:
Horizontal wind in accordance with SNiP 2.01.07;
Vertical from the own weight of the structures;
From the weight of household appliances and plumbing equipment hung on the structure;
Seismic (if the building is located in seismic areas).
5.2.5 The strength and stability of the adopted version of the structural scheme of the partitions should be checked by calculation for the action of wind load, taken equal to 0.2W 0 , where W 0 - calculated value of wind speed pressure, determined by SNiP 2.01.07.
5.2.6 The calculated seismic load taken into account in the calculations for seismic impacts is 6.5 for areas with seismicity 7, 8 and 9, respectively; 12.8 and 25.6 kg/m2.
5.2.7 To ensure the strength of the partitions when exposed to attachments, the provisions of the section should be taken into account of this Code of Rules.
5.2.8 The resistance of partitions to accidental impacts should be ensured by installing protective corner profiles at the outer corners.
5.2.9 The length of the partitions should not exceed 6 m, and the height - 3.6 m. Large partitions are recommended to be made from separate fragments, the dimensions of which should not exceed those indicated above, with the installation of a frame attached to the load-bearing structures of the building.
5.2.10 Interior partitions are designed as single, and between apartments as double, with the formation of an air gap, as well as with an additional layer of soundproofing material.
5.2.11 It is recommended to design partitions with the slabs installed with the groove facing up to ensure uniform distribution mounting adhesive at the tongue-and-groove joint.
If necessary, it is possible to install the slabs with the groove down.
The slabs must be placed staggered, with the end (vertical) joints offset by at least 100 mm.
Interfacing of partitions with other building structures
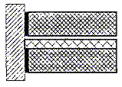
5.2.12 For partitions that are not presented regulatory requirements by soundco-insulation, it is recommended to use rigid coupling in places where they adjoin the enclosing structures directly through a solution of mounting adhesive (pictures - ).
5.2.13 For partitions that are subject to regulatory requirements for sound insulation, it is recommended to use an elastic connection between them and the building envelope (figures - ).
5.2.14 Elastic coupling should be performed by attaching the partition to walls, other partitions and ceilings with metal brackets and using an elastic gasket.
5.2.15 The horizontal installation spacing of metal brackets should not exceed 1335 mm for slabs of size 667´ 500 mm and 1800 mm with slabs size 900´ 300 mm; vertically - 1000 mm with slabs size 667´ 500 mm and 900 mm with slabs size 900´ 300 mm. In this case, at least three fastenings must be provided on each side of the partition.
Providing sound insulation
5.2.16 Required insulation index airborne noise Rw partitions made of gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs should be installed in accordance with the instructions SNiP 23-03.
5.2.17 The airborne noise insulation index of some types of partitions can be taken from the table when designing .
Table 5.2
|
Thickness of tongue-and-groove plate, mm |
Airborne noise insulation indexRw, dB |
|
|
Single layer |
||
|
Double layer with 40 mm air gap |
5.2.18 The airborne noise insulation index of two-layer partitions made of gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs with an additional soundproofing layer in all cases must be determined by testing in accordance with GOST 27296.
Fire technical characteristics of partitions
5.2.19 The fire resistance limit of single-layer partitions made of gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs according to the “Manual for determining the fire resistance limits of structures, the limits of fire propagation along structures and the flammability path” with slab thicknesses of 80 mm and 100 mm is respectively EI 130 and EI 160, and the structural fire hazard class is KO.
Figure 2 - Constructive decisions rigid connection of a single-layer partition with enclosing structures

Figure 3 - Constructive solutions for rigid coupling of a two-layer partition with enclosing structures
Figure 4 - Designs of single-layer nodes ( A) and two-layer ( B) partitions when rigidly adjacent to the wall and forming an angle
Figure 5 - Constructive solutions for elastic coupling of a single-layer partition with enclosing structures

Figure 6 - Constructive solutions for elastic coupling of a two-layer partition with enclosing structures
Figure 7 - Designs of partition assemblies with elastic coupling with enclosing structures
Figure 8 - Designs of pipeline passage units with a diameter of up to 60 mm ( A) and more ( B) through the partition and through the shaft (B)
Figure 9 - Constructive solutions for rigid ( A) and elastic ( B) junction of wall cladding with enclosing structures
Figure 10 - Designs of wall cladding units in areas of window openings ( A) And expansion joint (B)
5.2.20 According to SNiP 21-01 partitions made of gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs can be used in residential, public and industrial buildings of all degrees of fire resistance.
5.2.21 In places where partitions interface with water supply, steam and water heating pipelines, it is necessary to install a sleeve made of fireproof materials, ensuring free movement of pipes when the temperature of the coolant changes (Figure ).
5.2.22 When crossing a fire barrier with pipelines with a diameter of more than 60 mm, the pipeline should be insulated with a casing with a fire resistance of at least 0.5 hours at a length of 6.5 m from the plane of the partition.
5.2.23 When air ducts cross fire partitions, the walls of the air ducts must have fire protection that provides a fire resistance limit of at least 0.5 hours for buildings I and II degrees of fire resistance in accordance with SNiP 41-01.
5.3 Internal cladding of external walls
5.3.1 It is recommended to use internal cladding of external walls with gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs for additional heat and sound insulation.
5.3.2 Between the cladding and the wall, a layer of heat and sound insulating material may be additionally provided, the characteristics of which must be accepted based on the results thermotechnical calculation By SNiP 23-02 from the condition of inadmissibility of moisture accumulation in the wall over an annual period and moisture limitation for a period with negative average monthly temperatures.
5.3.3 The calculated value of the airborne noise insulation index with gypsum tongue-and-groove cladding should be determined in accordance with the instructions SNiP 23-03.
5.3.4 By analogy with partitions, the interface of the cladding with adjacent enclosing structures can be rigid or elastic (Figure ).
5.3.5 It is recommended to cover the gaps between the cladding and the wall at the junctions with the windows with gypsum fiber sheets GOST R 51829 which are attached to the cladding using dowels through a galvanized channel 40´ 75 ´ 40 ´ 2.0 mm. The channel, placed on the end of the slab, is secured to it with self-tapping screws. End gap gypsum fiber sheet and the window frame should be sealed with silicone or thiokol sealant (Figure ).
5.3.6 At locations expansion joints walls when facing them with gypsum boards with additional insulation thermal insulation material in the vapor barrier layer it is necessary to provide a compensator (Figure ).
5.3.7 It is recommended to attach the layer of additional thermal insulation to the wall using glue or expansion dowels.
5.3.8 When using cladding as a fire-retardant element, increasing the value fire technical characteristics walls, the actual fire resistance limit of such walls should be established by tests according to GOST 30247.1 , and the fire hazard class is according to GOST 30403.
6 TECHNOLOGY OF INSTALLATION AND CONSTRUCTION OF STRUCTURES FROM GYPSUM TONGUE-TOB BOARDS
6.1 Installation of partitions and cladding
6.1.1 It is recommended to install partitions during the finishing work. Work on wall cladding is also carried out during the finishing work process, when the wiring of electrical and sanitary systems is completed.
6.1.2 Before installing partitions and cladding, all construction work associated with “wet” processes must be completed. Installation must be carried out under dry or normal humidity conditions at an air temperature in the room not lower than +5 ° C before installing a clean floor.
6.1.3 Before installation, gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs must be kept at a temperature not lower than +5 °C for 4 hours.
6.1.4 Before starting work on installing partitions and cladding, dust and dirt must be removed from the base floor, walls and ceiling.
6.1.5 In accordance with the project, it is necessary to mark the position of the partition or cladding on the floor and use a plumb line to transfer it to the walls and ceiling. The position of the openings should also be marked on the floor.
6.1.6 If the floor surface is uneven, they must be eliminated with a leveling layer of cement-sand mortar brands not lower than 50.
6.1.7 When elastically connecting a partition or cladding with enclosing structures to the latter at the junction points assembly adhesive an elastic gasket is glued on. In this case, it is necessary to ensure the horizontal position of the gasket on which the bottom row of slabs should be installed. You should begin installing the slabs after the glue has set.
6.1.8 If the slabs are laid with the groove up, the ridge must be removed from all slabs in the first row using a roughing plane.
6.1.9 When installing the slabs of the lower row, the compliance of their position with the design one should be controlled using a rule and a level.
6.1.10 When laying subsequent rows, a mounting compound is applied in the groove of the bottom row of slabs and in the vertical end groove of the installed slabs.glue and each slab are pressed down using a rubber hammer. Excess glue that comes out is immediately removed and used in the future.
6.1.11 During the process of laying slabs, it is necessary to control the thickness of vertical and horizontal joints, which should not exceed 2 mm, and use a rule and level to check the flatness of the wall.
6.1.12 When laying slabs staggered, additional elements are used, obtained by cutting standard slabs into specified sizes hand hacksaw with a wide blade and large teeth or a special power tool.
6.1.13 For last row Boards with beveled edges should be used and, if necessary, they should be cut to fit the ceiling surface configuration.
6.1.14 The slabs of the top row, as a rule, should be laid on the previous row with the long side, but to reduce waste, they can also be laid with the short side, subject to obligatory spacing of the end joints.
6.1.15 When elastically connecting a partition or cladding with adjacent structures, the fastening bracket is installed in the groove of the slab and secured to it with self-tapping screws, and to the enclosing structures - with anchor dowels.
6.1.16 Openings with a height of no more than 1/4 of the height of the partition and the area of which does not exceed 1/10 of the area of the partition may be made by cutting into the mounted partition. It is recommended to make large openings during the installation of the partition. For an opening up to 800 mm wide, if only one row of slabs is placed above it, a mounting structure is fixed above the opening to ensure the design position of the slabs before the adhesive sets in the joints (Figure ). If the opening is wider, a lintel with a support depth of at least 500 mm should be installed above it.
6.1.17 Door frames should be secured in the partition opening using self-tapping (drilling) screws according to the drawings And .
6.1.18 When forming a corner and where partitions or facings intersect with each other, the slabs should be laid with overlapping joints below the row located (Figure ).
6.1.19 To protect against mechanical damage, a PU 31/31 corner protection profile is fixed to the outer corners of the partitions, which, during installation, is pressed into the pre-applied layer of glue, after which it is used with a wide spatula or a spatula for external corners Apply a leveling layer.
6.1.20 Internal corners should be reinforced using reinforcing tape, which is embedded in a layer of adhesive, and then a leveling layer is applied on top using an internal corner spatula.
Figure 11 - Installation diagram installation structure when constructing a doorway
6.1.21 To prepare for finishing, the joints of the slabs are puttied using a wide spatula, and after drying, they are treated with a manual grinding device.
6.2 Installation of electrical and low-current wiring and piping
6.2.1 For electrical and low-current wiring in a partition or cladding made of gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs, grooves are made using a groove maker, in which the wiring is sealed with gypsum mounting adhesive. In this case, the groove spacing must be no less than the thickness of the slab, the depth must not be less than 1 cm, and the thickness of the slab behind the groove must not be less than 40 mm or 50 mm for slabs with a thickness of 80 and 100 mm, respectively (Figure ).
6.2.2 Under the sockets, distribution boxes and switches in the partition or lining of the hole are drilled with an electric drill with a special attachment.
6.2.3 Not for pipelines large diameter The grooves are also cut out and then sealed with gypsum mounting adhesive. The amount of embedding and the distance between the grooves should not be less than those shown in the diagram (Figure ).
6.2.4 Large diameter pipes, as well as groups of pipelines and air ducts should be placed between the layers of a two-layer partition. In this case, after installing one layer of the gypsum partition, all engineering communications are fixed to it, and then the second layer of the partition is erected. The pipelines must not come into contact with the partition slabs.
7 FINISHING SURFACES OF STRUCTURES MADE FROM GYPSUM TONGUE-GRAVE PLATES
7.1 The surface of partitions and cladding made of gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs can be preparedsuitable for painting, wallpapering, cladding ceramic tiles or decorative plaster.
Drawing 12 - Design of door frame fastening units in a single-layer partition with an opening width of up to 900 mm ( A), up to 1600 mm ( B) and up to 2000 mm ( IN)
Figure 13 - Design of door frame fastening units in two-layer partitions with opening widths up to 900 mm ( A), up to 1600 mm ( B) and up to 2000 mm ( IN)

Figure 14 - Layout diagram of slabs at the intersection of partitions
Figure 15 - Schematic diagrams of the placement of pipelines, electrical and low-current wiring in partitions made of gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs
7.2 To improve the adhesion of the paint layer, the entire surface should be treated with KNAUF-Tiefengrund™ primer, which is applied using a roller or brush. Complete drying of the primer coating occurs after 3 hours.
The final finishing preparation of the surface should be carried out using the KNAUF-Finishpaste™ putty composition, which is applied to the surface in a thin layer with a wide spatula. After drying, the surface is sanded.
7.3 Water-based, oil-based, resin, polyurethane or epoxy paints. The use of lime paints and paints based on liquid glass is not allowed.
7.5 When finishing wallpaper, before pasting, it is recommended to treat the entire surface with KNAUF-Tiefengrund™ primer.
7.6 The surfaces of partitions and cladding made of moisture-resistant gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs in rooms with wet conditions should be finished with ceramic tiles on a pre-applied layer of KNAUF-Tiefengrund™ primer.
7.7 It is recommended to pre-coat the surface of structures exposed to direct moisture (in showers, near sinks) with KNAUF-Flechendicht™ waterproofing mastic, which is applied with a brush or roller, and glue the corners with KNAUF-Flechendicht™ sealing waterproofing tape.
7.8 After the waterproofing mastic or primer coating has dried, KNAUF-Fliesenkleber® tile adhesive, TU 5745-012-04001508-97, is applied with a notched trowel, onto which the ceramic tiles are laid.
7.9 The seams between the slabs are filled with grouting compounds, for which it is recommended to use the KNAUF-Fugenbunt™ compound.
8 BASIC SAFETY RULES DURING WORK
8.1 Construction of structures made of gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs should be carried out in compliance with the requirements SNiP 12-04.
8.2 Persons who have been instructed in safety precautions, industrial sanitation, trained in installation techniques and have a certificate for the right to carry out work should be allowed to install structures using gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs.
8.3 Workers must be provided with special clothing and personal protective equipment.
8.4 Work on the installation of structures using gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs is recommended to be carried out by specialized teams with experience in installing such structures and equipped with special tools.
8.5 The tools, equipment, fixtures and fittings used for the installation of structures used during the work must meet the safety conditions for performing construction and installation work. The recommended list of special tools is given in the appendix .
9 TRANSPORTATION AND STORAGE OF MATERIALS AND PRODUCTS
9.1 Gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs are transported by all types of transport in accordance with the rules for the transportation of goods in force for this type of transport.
9.2 The slabs are transported in packaged form. Transport packages are formed from slabs of the same type and size. Packaging schemes are established in the technological documentation.
By agreement with the consumer, transportation of slabs in unpackaged form is allowed.
9.3 When stored at the consumer's place, transport packages of slabs can be stacked on top of each other in accordance with safety regulations. In this case, the height of the stack should not exceed 2 m.
When loading, unloading, transporting and storing slabs, measures must be taken to prevent the possibility of damage and moisture. It is not allowed to load slabs in bulk or unload them by dropping them.
9.4 During the period of established negative temperatures, in order to avoid freezing of the slabs among themselves, packaging is done using cushioning material between the slabs.
9.5 The slabs should be stored in rooms with dry and normal humidity conditions, separately by type and size.
9.6 The manufacturer must guarantee that gypsum tongue-and-groove boards comply with all the requirements of the manufacturer for at least a year, subject to the conditions of transportation and storage.
9.7 Heat and sound insulating materials can be transported by any means of transport, provided they are protected from moisture.
9.8 Thermal and sound insulating materials should be stored in closed warehouses or under a canopy, provided they are protected from moisture.
9.9 Screws, dowels, metal plates for fastening can be transported by any type of transport, packed in boxes or boxes equipped with labels, and stored under a canopy.
10 ACCEPTANCE OF ASSEMBLED STRUCTURES FROM GYPSUM TONGUE-TOGGED PLATES
10.1 It is recommended that the designs of partitions and cladding made of gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs be adopted in stages with the execution of appropriate acts for hidden work (laying electrical and low-current wiring, laying heat and sound insulating materials and etc.).
10.2 The mounted structures of partitions and cladding must be smooth and smooth surfaces free of dirt, glue and putty compounds, unfilled seams and cavities. You should check for cracks and broken corners. Outgoing to front side The heads of screws, bolts and anchors must be recessed into the body of the slab.
10.3 Defects in the surfaces of partitions and claddings should not exceed the values given in the table .
10.4 In places where partitions and claddings interface with other enclosing structures and where they intersect with each other, putty must be laid without breaks along the entire interface contour to the full depth of the joint.
11 BASIC RULES FOR TECHNICAL OPERATION OF STRUCTURES MADE FROM GYPSUM TONGUE-TOGGED PLATES
11.1 The type of fastening element used should be selected depending on the weight of the objects hung on the partition or cladding.
11.2 Lightweight attachments and interior items are attached to partitions and cladding made of gypsum tongue-and-groove slabs using plastic anchor dowels. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the maximum permissible load per dowel indicated in the table .
11.3 To determine the maximum load on the dowel (elastic tension), it is recommended to use the formula
WhereF - maximum load (elastic tension) on the dowel, kN;
B - maximum weight of the suspended object, kN;
Table10.1
|
Permissible deviations during finishing |
|||
|
simple |
improved |
high quality |
|
|
Surface irregularities (detected when applying rules or a 2 m long template) |
No more than three deep or convex up to 5 mm |
No more than two deep or convex up to 3 mm |
No more than two deep or convex up to 2 mm |
|
Vertical deviation of the structure plane |
15 mm for the entire height of the room |
1 mm per 1 m, but not more than 10 mm over the entire height of the room |
1 mm per 1 m, but not more than 6 mm over the entire height of the room |
Table 11.1
|
Company manufacturer |
Brand |
Diameter, mm |
Depth, mm |
|
|
Fischer-Duebel S |
S8 |
8 |
55 |
0,12 |
|
S10 |
10 |
70 |
0,24 |
|
|
TOXCombi-Duebel |
Combi 10/50 |
10 |
60 |
0,30 |
|
Combi 12/60 |
12 |
70 |
0,46 |
|
|
Upat U Ultra-Duebel |
U8 |
8 |
55 |
0,20 |
|
U10 |
10 |
65 |
0,35 |
|
|
U12 |
12 |
75 |
0,50 |
|
|
HILTI Universalduebel HUD |
HUD8 |
8 |
55 |
0,15 |
|
HUD10 |
10 |
65 |
0,30 |
Figure 16 - Mounting points for communication equipment to a single-layer partition ( A) and two-layer ( B)

e - distance of the center of gravity of the hung object from the wall, cm;
P - number of fastenings;
A - support arm, see
11.4 Heavy attachments and objects must be secured using special fasteners such asIt is often recommended to use through anchors and bolts with steel washers (Figure ).
11.5 If partitions or cladding are damaged during operation from mechanical influences, leaks, etc. The cause of the damage must first be identified and eliminated.
11.6 If water gets into the cavities of two-layer partitions or into the gap between the cladding and the wall, it is necessary to drain standing water, for which, at the bottom of the partition or cladding, control holes are first drilled with a drill, and then, if necessary, an opening is cut out necessary to repair the damaged pipeline.
11.7 After repair work in the pipeline, the hole is sealed with standard gypsum boards or inserts cut from them.
APPENDIX A
LIST OF REGULATIVE DOCUMENTS REFERENCED IN THIS CODE OF RULES
SNiP 12-04-2002 Occupational safety in construction. Part 2. Construction production.
SNiP 21-01-97* Fire safety buildings and structures.
SNiP 02/23/2003 Thermal protection of buildings.
SNiP 2.03.11-85 Protection building structures from corrosion.
SNiP 2.01.07-85* Loads and impacts.
SNiP 41-01-2003 Heating, ventilation and air conditioning.
SNiP 03/23/2003 Noise protection.
GOST 10702-78* Rolled products from high-quality structural carbon and alloy steel for cold extrusion and upsetting. Technical conditions.
Many types of construction work can be significantly accelerated without loss of quality if modern technologies are used.
The construction of interior partitions using tongue-and-groove blocks as the main material can significantly reduce time costs. And when recalculating the cost per 1 m2, construction work will cost less than ordinary brickwork.
What are tongue-and-groove blocks?
Tongue-and-groove slabs are made from gypsum or silicate mixture. There are grooves and protrusions along the edges of the blocks for a more durable connection of the material to each other. The ridge of the block can be rectangular or trapezoidal.
In both options, the groove is quite securely fixed in the recess and does not allow the material to move.
The slabs can have a solid structure or with cavities inside. Hollow blocks have less weight and have increased heat and sound insulation, but in terms of mechanical strength such products are significantly inferior to solid products.
Both options can be used to make partitions, but if you plan to install massive shelves on a wall made of this material, it is recommended to purchase solid slabs.
Advantages of tongue-and-groove blocks
Like any building material, tongue-and-groove blocks have pros and cons.

TO positive characteristics This material includes:
- fire safety;
- vapor permeability;
- environmental friendliness;
- efficiency;
- does not require plastering;
- light weight.
Tongue-and-ridge partitions do not ignite even when exposed to high temperature, and when heated they do not emit toxic or foul-smelling substances. Thanks to these qualities, the material can be used without any restrictions for the construction of partitions for kitchens, rooms with installed heating equipment, including fireplaces and stoves.
The structure of the material does not prevent the penetration of steam, so the partitions can be equipped with tightly closing doors. In this case, no disturbances in the microclimate of the room will be observed.
Due to its relatively light weight, the structure does not require additional reinforcement of the base for the partition. Therefore, in comparison with solid ones, tongue-and-groove blocks turn out to be more preferred material for the construction of dividing structures in multi-storey buildings.
Disadvantages of the material
The disadvantages are:
- The need to perfectly level the floor under the partition before starting installation work.
- To get more robust construction It is required to install blocks in 2 rows.
- Indoors with high humidity it is necessary to install more expensive slabs.
- During operation it is formed a large number of dust and small waste.
- In direct contact with liquid, the stove quickly gets wet.
These are the main disadvantages that may arise when constructing walls from tongue-and-groove blocks.
If you need to quickly make a partition, the main purpose of which will be to physically delimit the space of the room. The use of this material is the most optimal, despite some imperfections in the building material.

Types of GWP
Tongue-and-ridge partitions can be made of the following types material.
Gypsum boards
Gypsum tongue-and-groove blocks, the price of which is always affordable, without compromising the quality of the product, allow construction work to be carried out as quickly as possible.
A tongue-and-groove comb, the dimensions of which are: height 50 cm, length 66.7 cm and thickness 8 cm, is enough to purchase in the amount of 2 - 3 dozen blocks for the manufacture of standard interior partitions.

Gypsum is environmentally friendly pure material, therefore, for people who care about their health, the use of building materials from these raw materials is the best option erection of walls in a residential area. Tongue-and-groove gypsum boards are made by casting using plasticizing additives, which are necessary to improve the strength of the product.
A significant disadvantage of gypsum tongue-and-groove blocks is the ability to absorb moisture upon contact with liquid.
If you need to make a partition in the bathroom or separate the kitchen from the living space, you should purchase special moisture-resistant gypsum boards. This type of tongue-and-groove blocks is made with the addition of cement and blast furnace slag, which can significantly reduce the hygroscopicity of the gypsum product.
Gypsum boards have good thermal insulation and can protect the room from extraneous sounds with a coefficient of up to 40 dB. Such positive traits are especially good when using gypsum hollow blocks. Plates of this design not only have good sound and heat insulating qualities, but also have less weight, which makes installation of partitions easier.
Silicate tongue-and-groove slabs
Silicate blocks, in comparison with gypsum material, have greater strength and have less water absorption. In terms of thermal insulation and sound absorption, such products are inferior to gypsum boards, but if you need to install massive shelves on the partition, then it is better to choose silicate blocks.

Tongue and tongue slabs of this type are made from a mixture of quartz sand and lime. To mix the mixture, use ordinary water.
The solution thus obtained is placed in an autoclave chamber for pressing and hardening under high temperature. In this way, a very durable building material with a thickness of 8-10 cm is formed, which can be successfully used for construction.
Despite high density material, silicate tongue-and-groove slabs are a “breathable” material, which allows you to provide a comfortable microclimate in the room.
Manufacturers and prices
To purchase gypsum or silicate tongue-and-groove blocks for partitions of proper quality, it is recommended to choose products from well-known manufacturers.
Knauf materials meet high safety and quality requirements, so if you decide to make a partition from tongue-and-groove blocks, you should choose this manufacturer. Knauf 667x500x100 in Leroy Merlin the price in the middle range of which does not exceed 250 rubles is ideal solution for the construction of interior partitions.

The moisture-resistant material from this company will cost only 20% more than a conventional block, but purchasing this type of slab is absolutely necessary when building walls in a damp room.
It is not only imported tongue-and-groove blocks for partitions that have good characteristics. Domestic producers The production of high-quality building materials of the highest quality has also been established.
The Russian company Volma produces a huge range of high-quality products, including tongue-and-groove blocks. Moisture-resistant Volma 667x500x80, the price of which is significantly lower than imported analogues, allows you to make a partition in the bathroom that is resistant to moisture.

At a low cost, Volma building materials are distinguished by their high strength and workmanship. When installed correctly, the use of this material allows you to obtain high-quality surface, which will not require overhaul During a long time.
You can compare the prices of PGP Knauf:
- full-bodied moisture-resistant 667x500x80 mm - 252 rubles;
- full-bodied 667x500x80 mm - 197 rubles;
- full-bodied moisture-resistant 667x500x100 mm - 293 rubles;
- full-bodied 667x500x100 mm - 235 rub.
- hollow moisture-resistant 667x500x80 mm - 202 rubles;
- full-bodied 667x500x80 mm - 190 rubles;
- full-bodied moisture resistant 667x500x100 mm - 266 rubles;
- full-bodied 667x500x100 mm - 233 rub.
Installation features
When constructing partitions, it is important not only to purchase quality material, but also to implement correct installation blocks.

To carry out installation work, it is necessary to prepare following materials and tools:
- Sand-cement mortar.
- Tongue-and-groove slabs.
- Glue.
- Mounting brackets.
- Gypsum solution.
- Seal.
- Primer.
- Dowels and screws.
- Building level.
- Putty knife.
- Screwdriver.
- Hacksaw.
- Rubber mallet.
Installation work is carried out in the following sequence:
1. Preparing the base
The base under the tongue-and-groove slabs must be perfectly level. Small cracks and irregularities on the surface can be sealed with cement mortar, and the sagging can be removed with a spatula. In case of significant curvatures, it will be necessary to level the base with a concrete screed.

The walls and ceiling at the junction with the blocks, if necessary, also need to be repaired, and after the solution has dried, a layer of primer must be applied.
2. Installation of the first row
The first row of blocks should be installed as level as possible to ensure the vertical position of the partition. For this purpose, it is necessary to install a cord between the walls at a height of 25-30 cm.

The first row is installed on a special seal, which is pre-glued to the surface of the base. Installation of the first row should be carried out using a level and special brackets for more reliable fastening slabs to the wall.
3. Installation of the next rows
Subsequent rows are installed with offset seams. To ensure greater strength, it is recommended to install rows in increments of 0.5 block lengths. The slabs of subsequent rows are also attached to the wall using brackets.

To securely fix the plates, glue is used, which is applied at the junction of the materials. Each subsequent row should be installed only after the glue of the previous row has set.
4. Installation of the last row
It is necessary to leave a technological gap of about 2 cm between the last row and the ceiling. And to ensure reliable fixation, attach the slabs to the ceiling using staples and anchor bolts. When the slabs are fixed in this way, the gap between the wall and the ceiling is sealed with polyurethane foam.

Conclusion
The construction of partitions from tongue-and-groove slabs allows you to save a lot of time, and given the small thickness of the slab, such a redevelopment will not “eat up” too much area of the room.
Therefore, if you need to quickly build an additional wall, then the best option there will be application of technology using these building materials.