In a competitive environment, market volatility and a rapidly changing marketing environment, an entrepreneur needs to take right decisions. He must clearly understand at what stage of development his business is, what competitive advantages he has something to be afraid of, what disadvantages negatively affect the development of his business, and so on. Many techniques and technologies are used in marketing, one of which is SWOT analysis, a simple and effective tool making key management decisions.
Why SWOT analysis is needed
This technology helps to analyze a problem, a product, a business situation, everything that can be analyzed as an object. It becomes clear where the company should move in its policy, what actions the manager needs to plan, answers are received about the effectiveness or inefficiency of the company's actions. The final result of the SWOT analysis is the development of a strategy for the further development of the organization (project), or correction of its course, taking into account the existing market reality. The recommended interval for conducting analytics is once a quarter.
Pros and cons of analysis
The main advantage of this tool is simplicity. Doesn't need to be possessed special knowledge or make complex marketing calculations. To do a SWOT analysis, do correct conclusions, plan relevant events - it is enough for analysts to have minimal awareness of the internal and external business space of the company.
The undeniable benefit of the method is its wide application, the prospect of its use not only in the economic or marketing sphere. Where it is necessary to assess the situation with conclusions and solutions, this tool will help. This applies to all aspects of human life and activity.
The third clear advantage is that this analysis allows you to collect an impressive information base on the issue under consideration.
Accordingly, the more information - the more versatile it is possible to look at the problem, consider it from different angles, find more solutions, ways of implementation. In the process of collecting information, a variety of factors that affect the enterprise are revealed, therefore, it is possible to collect completely different analytical material and generalize according to certain features, expanding the variability of decision-making methods.
The disadvantages of the analysis include the relevance of the results for a certain date or period of time. As a result of the analysis, the alignment of forces on the problem at the time of the study is shown, and the situation on the market often changes at lightning speed. Decisions based on the results of the analysis carried out require prompt implementation, since tomorrow they may become irrelevant.
From the point of view of quantitative indicators and evaluation criteria, the method is not informative enough. It only sets a vector, showing a fairly general picture of the problem (probability), while not giving a quantitative assessment and not allowing any qualitative comparisons.
And the final disadvantage of this analysis: the analysts filling the SWOT matrix can also look at the source data from different angles vision, as a result of which, the objectivity of the final analysis data may be lost. It is recommended to involve more than one analyst, but work as a team to comprehensively cover the source data for analysis. A team of 4-8 analysts and a SWOT moderator are practicing. Decision makers are present as well as persons representing all departments involved in the general business of the company. Comprehensive analytics usually takes from 8 to 32 working hours, not counting the preparation for the event itself.
Structure and decoding of the abbreviation
The name is an abbreviation of capital letters for the names of four English words:
S - strength(from English Strength, power) - significant qualities of the Company, internal analyzed environment),
W-weakness(from English. Weakness) - insufficient qualities of the Company, internal analyzed environment. Both of these factors are held relative to the Consumer.
O-opportunities(from English Perspective) - prospects for the Company, the external analyzed environment,
T - threats(from English. Threat) - dangers for the Company, the external analyzed environment. These factors are considered in relation to representatives of the competitive market environment.

Types of analytical matrices
Short SWOT (four fields)
A four-field SWOT analysis captures the state of affairs, the situation in the external and internal environment of the company. The analytical group must divide into four sectors all the factors that reflect the current situation in the company and reflect its capabilities.
|
STRENGTH(significant qualities of the company, having superiority over other companies in the same industry). The company can influence these internal factors. |
WEAKNESS(insufficient qualities of the company, weakening its position in the industry, compared with other companies). The company can influence these internal factors. |
|
PERSPECTIVE(probabilities and market prospects for the company, unpredictable positive probabilities). The Company cannot influence these external factors. |
DANGER(some market dangers, unpredictable negative probabilities). The Company cannot influence these external factors. |
If analysts are not ready to split into four cells, all factors (even insignificant ones) are split into two:
|
STRENGTH AND WEAKNESS |
PROSPECTS AND DANGERS |
Further, the data is redistributed into four fields and, in each group, about 5-8 key factors are highlighted. To determine priorities by factors, each participant is provided with virtual 20-32 points to be awarded, 1 point for each field. Thus, the data array is compressed to the required number of factors in four fields.
The classical (nine-field) matrix helps to develop a strategy based on the data of the four-field matrix. The STRENGTH, WEAKNESS, PERSPECTIVES and DANGERS fields are filled with data from the four-field matrix. Thus, cross-links of the type "STRENGTH and PERSPECTIVE", "POWER and DANGER", "WEAKNESS AND PERSPECTIVE", "WEAKNESS and DANGER" are formed. These are the strategy development vectors:
- "POWER and PERSPECTIVES" - development of the company's GROWTH strategy;
- "POWER and DANGERS" - development of a strategy for the PROTECTION of the company;
- "WEAKNESS AND PROSPECTS" - development of a strategy for IMPROVING the company;
- "WEAKNESS AND DANGERS" - development of a strategy to MINIMIZE the company's PROBLEMS.
|
OUTLOOK: |
DANGERS: |
|
|
STRENGTH: |
Effective use capabilities of the organization, its strengths, to maximize the positive opportunities provided by the market |
Effective use of the strengths of the organization to offset the negative aspects emanating from the market |
|
WEAKNESS: |
Eliminate the weaknesses of the organization, due to the opportunities that the market provides |
Reversing weaknesses and minimizing market threats |
SWOT Analysis Examples
Business (on the example of a car service)
- Four-field matrix
|
External factors |
|
|
STRENGTH: |
PERSPECTIVE:
|
|
WEAKNESS:
|
DANGER: |
- Nine-field matrix
|
OUTLOOK:
|
DANGERS:
|
|
|
STRENGTH:
|
Effective use of the organization's capabilities, its strengths, to maximize the positive opportunities provided by the market
|
Effective use of the strengths of the organization to offset the negative aspects emanating from the market
|
|
WEAKNESS:
|
Eliminate the weaknesses of the organization, due to the opportunities that the market provides
|
Reversing weaknesses and minimizing market threats
|
Product (on the example of a brick)
- Four-field matrix
|
STRENGTH:
|
PERSPECTIVE:
|
|
WEAKNESS:
|
DANGER:
|
- Nine-field matrix
|
OUTLOOK:
|
DANGER:
|
|
|
STRENGTH:
|
|
|
|
WEAKNESS:
|
|
|
Entrepreneur
- Four-field matrix
|
Internal factors |
External factors |
|
STRENGTH:
|
PERSPECTIVE:
|
|
WEAKNESS:
|
DANGER:
|
- Nine-field matrix
|
OUTLOOK:
|
DANGER:
|
|
|
STRENGTH:
|
|
|
|
WEAKNESS:
|
|
|
Success in life is probably possible when you use your talents to the fullest. You will also need to deal with your weaknesses so that they do not interfere with your life and work. It was for these purposes that the SWOT analysis was transferred to the field of self-development.
What makes the SWOT model especially powerful is that it helps to identify opportunities in our world that don't appear to be at first glance. It will also help in the development of your business or your work. The model considers four characteristics:
- S-Strengths ( strengths)
- W - Weaknesses ( weak sides)
- O - Opportunities (opportunities)
- T - Threats (threats)
Let's consider them in more detail.
SWOT
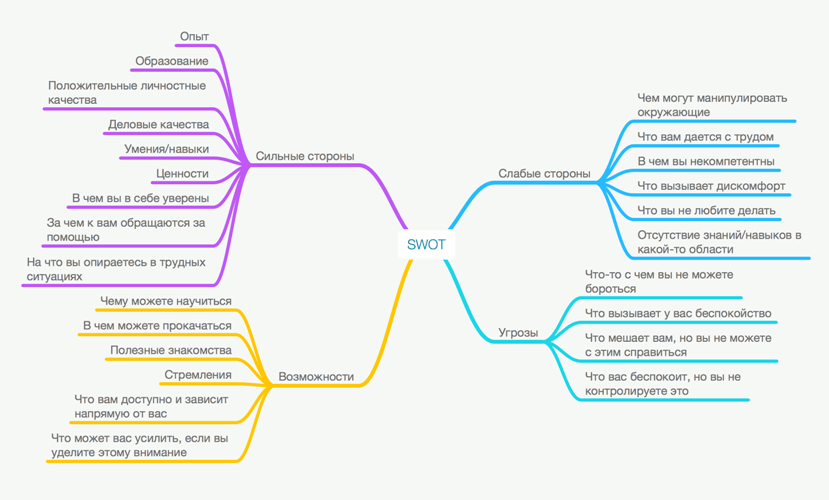
Strengths
- What strengths do you have that others don't? For example, skills, education, connections.
- What do you do better than others?
- What resources do you have access to?
- What other people think is yours strong point?
- What accomplishments are you most proud of?
- What values do you believe in that others do not believe in?
- Do you have connections with important people?
This list of questions is quite objective, because it takes into account not only your opinion, but also the opinion of others. Knowing your strengths makes a person happier and allows you to apply them in your work.
If you are having trouble identifying your strengths, write down a list of your personal characteristics. Some of them will be your strengths. Especially appreciated are those that others do not have. For example, if you know her very well and are surrounded by people who know her even better, this may not be your strong point. But if you are the kindest and most tactful among all your friends (and they confirm this), then it's them.
Weak sides
- What tasks do you most often avoid because you feel insecure?
- What exactly do people around you consider your weaknesses?
- Are you absolutely confident in the usefulness of your education and skills? If not, what are you weakest at?
- What are your negative work habits? For example, you are often late, disorganized, short-tempered, or unable to cope with.
- Do you have character traits that constantly hold you back and prevent you from progressing? For example, it could be a fear of speaking in public, even though this is your main responsibility.
Again, weaknesses are seen not only from your point of view, but also from the point of view of others. Listen to what is being said about you. Even if people are wrong, you are perceived that way, which means they will treat you accordingly.
Capabilities
- What new technologies will help you? What can you find on the Internet from what you need?
- Is your industry growing? What advantage can we get from this?
- Do you have strategic contacts with other people who will help you?
- What trends and patterns do you see in the world or your company that will help you in the future?
- Have your competitors failed trying to achieve something important? If so, what conclusions can you draw to avoid their mistakes?
- What does your company need?
- What are your customers and suppliers complaining about? What can you offer them?
You may find the following options useful:
- , courses, conferences.
- A new role in a company or project can enhance your existing skills and acquire new ones.
- learn English language in order to have more business opportunities.
Re-examine your sides and think about how to use them most effectively in order to open up new opportunities.
Threats
- What difficulties do you face at work?
- Are there colleagues who compete with you?
- Does the essence of your work and the requirements for it change?
- Is the development of new technologies a threat to you and your profession?
- Can your weaknesses become a threat to your future?
It is important to know what threats you face or will face in life, because being aware of them will help you figure out which strengths to develop and which weaknesses to get rid of.
Example
Here's what your SWOT analysis might look like:
Strengths
- I'm a creative person. I often surprise clients and boss with new ideas.
- I can communicate with people and convince them.
- I have the ability to ask the right questions.
- I can think and often make the right conclusions.
Weak sides
- I have an impulsive need to complete the things on my list as quickly as possible. This affects the quality of work.
- I lose myself in stressful situations.
- I have a fear of public speaking.
Capabilities
- I'm organizing a conference next week. it great chance meet new and important people.
- Our art director is going on maternity leave soon. it a great opportunity develop my skills.
Threats
- I work too hard, so my creativity drops.
- A fall in the level of the economy can lead to a fall in our market.
- My colleague, who knows how to speak in public, and in general is more sociable than me, is applying for the position of art director.
By learning the four components, you can find the solution and be successful. Remember that the model itself is not capable of doing miracles, it only indicates and hints to you what needs to be done.
SWOT analysis is a great way to find a starting point and explore yourself. It allows you to face the truth, albeit sometimes unpleasant. SWOT empowers you to focus on strengths, minimize weaknesses, avoid threats, and seize opportunities.
We wish you good luck!
Strategy development begins with an analysis of the external and internal environment. The starting point for such an analysis is the SWOT analysis, one of the most common types of analysis in strategic management. SWOT analysis allows you to identify and structure the strengths and weaknesses of the company, as well as potential opportunities and threats. This is achieved by comparing internal forces and weaknesses of their company with the opportunities that the market gives them. Based on the quality of compliance, it is concluded in which direction the organization should develop its business, and ultimately the allocation of resources to segments is determined.
The purpose of the SWOT analysis is to formulate the main directions for the development of the enterprise through the systematization of the available information about the strengths and weaknesses of the company, as well as potential opportunities and threats.
Tasks of SWOT-analysis:
Identify strengths and weaknesses compared to competitors
Identify opportunities and threats in the external environment
Associate strengths and weaknesses with opportunities and threats
Formulate the main directions of enterprise development
SWOT Analysis Basics
SWOT is an abbreviation of 4 words:
S trength - strength: an internal characteristic of the company that distinguishes this company from competitors.
W eakness - weak side: internal characteristic a company that looks weak (underdeveloped) in relation to a competitor, and which the company has the power to improve.
O pportunity - opportunity: a characteristic of a company's external environment (i.e. market) that provides all participants in this market with the opportunity to expand their business.
T hreat - threat: a characteristic of the external environment of the company (ie the market), which reduces the attractiveness of the market for all participants.
SWOT analysis in general form is built using the following table.
Table 1. General form of SWOT analysis
Elements of the internal environment: strengths and weaknesses
Under the strengths and weaknesses can hide a wide variety of aspects of the company. The categories most frequently included in the analysis are listed below. Each SWOT is unique and may include one or two of them, or even all at once. Each element, depending on the perception of buyers, can be either a strength or a weakness.
Pricing
Promotion
Marketing Information/Intelligence
Service/staff
Distribution/Distributors
Trademarks and positioning
Manufacturing/engineering
Sales and marketing
Processing orders/transactions
Research and development
Distributors
Marketing
After-sales service/service
Service/customer service
Marketing
Engineering and new product development. The closer the connection between marketing and technical department becomes, the more important these elements will be. For example, a strong relationship between the new product development team and the marketing department allows direct use of customer feedback in the design of new products.
Operational activities
Staff. This includes the skills wage and bonuses, training and development, motivation, working conditions of people, staff turnover. All of these elements are central to the successful implementation of a customer-focused marketing philosophy and marketing strategy. The role of personnel in the following areas is being investigated.
Management. Sensitive and often controversial, but sometimes requiring changes, management structures directly determine the success of the implementation of a marketing strategy. Such aspects should be reflected in the analysis.
Company resources. Resources determine the availability of people and finance, and thus affect the company's ability to capitalize on specific opportunities.
Situational, or SWOT (SWOT) analysis(the first letters of the English words strengths - strengths, weaknesses - weaknesses, opportunities - opportunities and threats - dangers, threats), can be carried out both for the organization as a whole and for certain types business. Its results are further used in the development of and .
Analysis of strengths and weaknesses characterizes the study of the internal environment of the organization. The internal environment has several components, each of which includes a set of key processes and elements of the organization (types of business), the state of which together determines the potential and the opportunities that the organization has. The internal environment includes financial, production and personnel and organizational components.
Since it does not have a clear manifestation, its analysis on a formal basis is very difficult. Although, of course, one can try to expertly evaluate such factors as the presence of a mission that unites the activities of employees; the presence of certain common values; pride in your organization; a motivation system that is clearly linked to the results of the work of employees; psychological climate in the team, etc.
- S- strenghts - strengths;
- W- weaknesses - weaknesses;
- O- opportunities - opportunities;
- T- threats - dangers, threats;
SWOT analysis is an analysis of the strengths and weaknesses of the company, and an assessment of the opportunities and threats in the way of its development.
SWOT Analysis Methodology involves first identifying strengths and weaknesses, as well as threats and opportunities, and then establishing chains of links between them, which can later be used to formulate organizational strategies.
First, taking into account the specific situation in which the organization is located, a list of its weaknesses and strengths is compiled, as well as a list of threats (dangers) and opportunities.
Next, a connection is established between them. For this, a SWOT matrix is compiled. On the left, there are two sections (strengths and weaknesses), in which, accordingly, all the strengths and weaknesses of the organization identified at the first stage of the analysis are entered. At the top of the matrix, there are also two sections (opportunities and threats), in which all identified opportunities and threats are entered.
SWOT matrix
SIV- Power and opportunity. A strategy should be developed to use the strengths of the organization in order to capitalize on opportunities. For those couples who ended up on the field SLV, the strategy should be built in such a way that, due to the emerging opportunities, try to overcome the weaknesses in the organization. SIOUX(Power and Threats) - develop a strategy that should use the strength of the organization to overcome threats. SLN(Weakness and threats) - develop a strategy that would allow the organization to get rid of weaknesses and prevent the impending threat.
For successful application It is important for the SWOT methodology to be able not only to reveal threats and opportunities, but also to try to evaluate them in terms of how important it is for the orientation to take into account each of the identified threats and opportunities in the strategy of its behavior.
To assess the opportunity, the method of positioning each specific opportunity on the opportunity matrix (Table 2.1) is used.
This matrix is built as follows: the degree of influence of the opportunity on the organization's activities (strong, moderate, small) is postponed from above; on the side - the probability that the organization will take advantage of this opportunity (high, medium, low). Received within the matrix ten fields of possibilities have different meaning for the organization. Opportunities falling on the fields "BC", "VU" and "SS" have great importance for the organization, and they must be used. Opportunities falling on the fields "SM", "NU" and "NM" practically do not deserve attention. With regard to opportunities that fall into the remaining fields, management should make a positive decision on their use if the organization has sufficient resources.
Table 2.1 Capability MatrixA similar matrix is compiled for hazard assessment (Table 2.2). Those threats that fall on the "VR", "VK" and "SR" fields pose a very great danger to the organization and require immediate and mandatory elimination. Threats that have fallen into the "BT", "SK" and "NR" fields should also be in the field of view of senior management and be eliminated as a matter of priority. As for the threats that are on the fields of "NK", "ST" and "VL", a careful and responsible approach to their elimination is required here.
Table 2.2 Threat MatrixIt is advisable to conduct this analysis by answering the following questions in relation to opportunities and threats in three areas:
- Determine the nature of the opportunity (threat) and the reason for its occurrence?
- How long will it exist?
- What power does she have?
- How valuable (dangerous) is it?
- What is the extent of its influence?
To analyze the environment, the method of compiling its profile can also be used. This method is convenient to use for compiling a profile of the macroenvironment, the immediate environment and the internal environment. Using the method of compiling a profile of the environment, it is possible to assess the relative importance for the organization of individual factors.
The environment profiling method is as follows. Separate environmental factors are written out in the environment profile table (Table 2.3). Each factor is given by expert way:
- assessment of its importance for the industry on a scale: 3 - strong importance, 2 - moderate importance, 1 - weak importance;
- assessment of its impact on the organization on a scale: 3 - strong, 2 - moderate, 1 - weak, 0 - no effect;
- assessment of the direction of influence on a scale: +1 - positive influence, -1 - negative influence.
Then all three expert opinions are multiplied, and an integral assessment is obtained, showing the degree of importance of this factor for the organization. Based on this assessment, management can conclude which of the environmental factors are relatively more importance for their organization and, therefore, deserve the most serious attention, and which factors deserve less influence.
From this article you will learn:
- What types of SWOT analysis method exist
- When should you not use SWOT analysis?
The SWOT analysis technique has become very popular due to its simplicity and wide applicability. It can be used to assess the likely consequences rational decisions in almost any area: both in business when developing a company development strategy, choosing a marketing policy, etc., and in privacy. The SWOT analysis method assumes that before making a decision, the situation was studied and understood. Let's look at it in more detail.
What is the essence of the SWOT analysis method
SWOT analysis is a way to assess the current situation in the business and the prospects for its development, identifying four key aspects: Strengths - strengths, Weaknesses - weaknesses, Opportunities - opportunities and Threats - threats.
Two of them - strengths and weaknesses - characterize the state of the internal environment of the company at the time of the analysis. The remaining aspects - threats and opportunities - relate to the external environment in which the business operates and which the entrepreneur or head of the firm cannot directly influence.
The method of conducting a SWOT analysis allows you to describe the situation clearly and structured, to conclude whether the company is developing in the right direction, what risks should be protected from and how exactly to implement it, what is the potential of the enterprise.
The SWOT analysis method is based on four main questions:
- What can a businessman (organization) do?
- What would he like to do?
- What is generally possible in the current conditions?
- What actions are expected from the company by its environment – clientele, partners, contractors?
By answering these questions, you can determine:
- advantages of the company, its trump cards that can be used in the development strategy;
- vulnerabilities that can be eliminated, compensated;
- prospects, open paths company development;
- dangers and ways to protect yourself from them.
Why you need a SWOT analysis method
SWOT analysis is simple and universal method, widely used in entrepreneurial activity and not only. In business, when planning and developing a strategy, it can be used both separately and in conjunction with other marketing tools, which makes it very convenient for company managers and private entrepreneurs.

Outside of business, the SWOT analysis method allows you to identify priority areas for applying efforts (this applies to both professional and personal development), to find your true life goals and priorities in labor activity and relationships.
In relation to business, SWOT analysis is used to:
- collecting, summarizing and analyzing information about competitors through Porter models, PEST and other marketing methods;
- creation step by step plan implementation of the business strategy, development of its main directions and appointment of persons responsible for the implementation;
- competitive intelligence (search for the strengths and weaknesses of competitors) to form an effective development strategy.
Thus, wherever it is necessary to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of something (commercial activity, enterprise, individual), there is a place for the SWOT analysis method. Its product can be both a business strategy and a program for professional or personal growth.
Types of SWOT analysis method
- Express version of SWOT-analysis. It occurs most often and is used to detect the main strengths of the company and its vulnerabilities. External threats and opportunities are also identified. This type of method is the easiest to use and gives a clear result.
- Summary SWOT analysis. The focus is on accounting and systematization of the main indicators of business performance in this moment and its future prospects. A summary SWOT analysis is good because it allows you to quantify the factors identified by other methods included in the strategic analysis toolkit, to form a strategy and action plan aimed at achieving the main goals of the company.
- A mixed SWOT analysis is an option that combines the first two. There are at least three of its varieties, in which the factors of influence are structured in the form of tables and form a cross matrix. However, the analysis of these types does not give a quantitative assessment of certain indicators. Thanks to the summary SWOT, you can deeply explore the received data and come to an accurate result.
SWOT analysis method by example
The main matrix of the SWOT analysis is as follows:

Consider this situation: individual entrepreneur is going to sell pies to grandmothers in small batches (and they, in turn, will resell them to the final buyer).
Here is how you can apply the SWOT analysis method to it:

Note that if the target audience is, for example, schoolchildren who buy pies for themselves (and not grandmothers-traders), then the SWOT analysis must be carried out again, since the initial data have changed.
SWOT project analysis
First of all, decide what goals you are going to achieve through the method, what tasks you face. If the project is devoid of goals and non-specific, the SWOT analysis will fail: there will simply be no place to take the initial data from.
Find potential strengths in your future (or existing) business. Make them up full list and proceed to analyze each of them. What characteristics and features make your idea realistic and promising? Are the means and tools with which you intend to implement your strategy effective, and by what means? How much a good entrepreneur(or leader) are you yourself? What resources and assets are available to you? What do you manage to do better than your competitors? In general, conduct an audit and evaluate your capabilities.

Then, using the same method, you need to analyze the shortcomings of the business project under consideration. What factors hinder the solution of urgent problems? What business skills do you personally lack and how can they be “pumped”? What is the main vulnerability of your enterprise and personally you as a person and leader? What factors should be avoided? What can prevent you from taking advantage of the opportunities and benefits to achieve your goals?
The next step in the SWOT analysis is to list the available prospects for your project. You probably already actively use some of these favorable environmental factors to promote and optimize your business, list them. Don't forget potential opportunities. Describe the market situation in your niche. Think about what tools, tools, methods and benefits can be applied to make your project unique and in demand.
After that, proceed to the description of existing external dangers and threats. Which of these factors are or could be preventing you from achieving your intended outcome? Is there a large number of your competitors, enemies, ill-wishers who can harm the business and prevent it from developing? In the SWOT analysis method, threats and opportunities are always related to the external environment, and strengths and weaknesses are always related to the project itself.
When all the lists are compiled, proceed to the formation of conclusions and conclusions. They should provide answers to a number of important questions about how to competently use your strong positions how to eliminate deficiencies and problem areas how to take advantage of the opportunities that have opened up in practice, how to minimize risks and avoid dangers.

Listing, cataloging and studying these four groups of factors is not the main part of the SWOT analysis method. The most important thing happens later, when the data has already been collected and structured: finding ways to turn problems into advantages, make weaknesses strong, and external threats to make them serve for the benefit of their business.
If at this stage it becomes clear what measures and steps need to be taken, be sure to plan them for the near future and actively begin to implement them.
Rules of the SWOT analysis method
SWOT analysis seems to be a simple, even primitive method, but in practice, building a matrix can be difficult. The problem lies in the quality of the initial data: if they are outdated, or initially unreliable (which often happens when we collect information about the external environment), or too abstract and generalized, then the method will not lead to the desired result.
That's why practical use SWOT analysis requires following some important rules:
- Limit the scope of the study to each of the quadrants. Analysis of the business as a whole will turn out to be too divorced from practice and, as a result, useless, because in order to develop a strategy, information is needed on very specific aspects of the functioning of the enterprise. It is worth focusing on each of them and subjecting them to a SWOT analysis.
- Decide on the wording: what you will consider a strength, what a weakness, and what you will attribute to opportunities and risks. Internal factors - the strengths and weaknesses of the company - can be controlled directly, but it is impossible to influence external ones. Therefore, these areas - inside the business and outside it - must be clearly separated, and, for example, internal problems should not be written down as threats, and opportunities should not be considered strengths.
- When analyzing advantages and vulnerabilities, look at your project from the outside, as a client or competitor. If something is an advantage for the consumer and motivates him to buy the company's products, then this is a strength.
If some services or product items offered by your company are more popular than similar products and services of competitors, this is also a business advantage. That is, both strength and weakness are determined by the market, and not by the manager-analyst's ideas about how to do it right. When the list of advantages and disadvantages grows too large, it is useful to rank them in order of importance (from the perspective of the consumer).
- Use a variety of but reliable information sources. Try to be objective when conducting a SWOT analysis. Best Option: first carry out extensive marketing research, and then use this method, but this is not always available. However, you can conduct monitoring on your own (using questionnaires, analysis of publications about the company in the media, etc.).
This task should be done by several people, since the personal preferences of each significantly limit the scope of the parameters considered. In the course of collecting and analyzing data, it is desirable to exchange ideas and guesses so that the work can be done in groups.
- Formulate your thoughts as clearly and specifically as possible, avoid ambiguity and unnecessary phrases. The quality of the application of SWOT analysis as a method depends on the accuracy and capacity of the formulations. For example, the term " modern equipment» is very blurry: it can hide both new machines in the shops and new technologies for communicating with suppliers.

- identification of the dynamics of the position of the enterprise in the market environment, among competing firms;
- more than deep analysis activities of the company and the construction of strategic plans in accordance with them;
- creation of several strategies of behavior in the market (for the most probable scenarios of development of events).
These can be options such as the elimination of threats (the third and fourth quadrants of the SWOT matrix), the continuation of the current course (without changes, since everything is fine anyway), the optimization of the use of resources and the development of reserves (the first and second quadrants).
