Flat roofs nowadays are undeservedly forgotten and not spoiled by the attention of developers. In private housing construction, they are found mainly in the southern regions, where heavy rains and snowfalls are rare. Hip roofs, on the contrary, have firmly established themselves in the projects and minds of homeowners.
This state of affairs can be explained simply: until recently, builders did not have reliable and durable waterproofing.
Standard roofing felt - cardboard impregnated with bitumen - cannot resist moisture and temperature changes for long. Even a thick 4-layer coating from it has to be changed after 6-8 years.
Today, interest in flat roofs is beginning to grow.
There are several reasons for this:
- Economic benefit. The cost of arrangement is lower than that of a tent structure (more simple design and smaller area);
- Additional usable space. There is the possibility of its rational use (flower garden, playground, recreation area, swimming pool);
- Availability of maintenance and operation (cleaning drains, installing air conditioners, antennas, inspecting coatings, ventilation and smoke ducts);
- A layer of snow acts as additional thermal insulation, reducing heating costs.
- Original appearance building.
Types of flat roofs
Strictly speaking, you will not see a completely flat roof on a building. Any of them has a minimum slope of 1 to 4%, necessary for precipitation runoff.
There are four types of flat roofs:
- unexploited;
- exploited;
- green (lawn);
- combined.
Unused roofs are found on industrial buildings.

Operated roofs have found application in public and private construction. They are equipped with recreation areas, cafes and restaurants, and used as parking lots and helipads.

Green (lawn) coverings are made to decorate buildings, as well as when there is not enough space on the site. In addition to the aesthetic function, they perform an important practical task. A layer of plant turf is an excellent heat and sound insulator.

Combined roofs with a flat surface are the most common option. Comfortable stay on fresh air Surrounded by green grass and flowering plants, everyone likes it.
According to the method of drainage, houses with a flat roof are divided into two types:
- With internal drain;
- With external water discharge (along the perimeter of the roof).

Internal drainage is cheaper than external drainage because it does not require a large number of gutters, pipes, funnels and high-rise work to install them. It is more difficult to execute. Errors in creating a slope and poor-quality sealing of joints lead to leaks and damage to the integrity of the protective layer of waterproofing.
In operation, flat coverings with internal drainage are more profitable. In winter, icicles do not grow on the eaves of such a roof. Drainpipes run inside the building and therefore do not freeze. Cleaning debris funnels is easier and easier than hanging gutters.
Device Features
According to the method of arrangement and arrangement of structural layers, experts distinguish two types of flat roofs:
- Classic;
- Inversion.
The classic roofing “pie” is equipped using the following technology:
- a slope is made from cement-sand mortar on reinforced concrete floor slabs;
- lay vapor barrier and insulation;
- lay down waterproofing membrane or roofing felt carpet;
- if the coating is to be used, the waterproofing is protected with ceramic tiles.

Classic flat roof structure
The main disadvantage of the traditional design is the vulnerability of the outer insulating layer from solar ultraviolet radiation and temperature changes.
Working to solve this problem, engineers came up with the idea of an inversion coating. In it, the main structural elements (insulation and waterproof membrane) are swapped. Waterproofing is hidden under polystyrene foam, which external influences protected by a gravel ballast layer or a tile finish.

Inversion coating design
The technology of work is changing accordingly. A waterproof carpet made of roofing felt or EPDM membrane is glued to the slab or spread on it, fixing it in places adjacent to the parapet.
The slope in this case is created in one of two ways:
- Mortar screed on the slab;
- Insulation, changing the thickness of its installation.

Installing thermal insulation on a flat roof
Water intake funnels and pipes are installed at the lowest points of the slope. In addition to them, ventilation is installed to remove water vapor that accumulates in the area of contact between the vapor barrier and the insulation.

When arranging a covering designed for planting plants, the structure is supplemented with a top layer of waterproofing. Drainage layers of gravel are poured over it, geotextiles are laid and a fertile layer of soil is poured.
In addition to roofing coverings laid on reinforced concrete slabs, designs for houses with a flat roof on wooden beams have been developed.

Construction technology in this case may include the following operations:
- Beams are mounted on the walls in increments of 50-100 cm, fixing them to the masonry with anchor pins. The cross-section of the beams depends on the span width, the design load and can range from 10x20 cm to 15x25 cm;
- Lay on beams OSB boards, tightly joining them together;
- Spread the waterproofing membrane in 2 layers, carefully gluing the joints of the sheets.
- Thermal insulation is made from durable (extruded) foam, gluing it to the membrane. A slope for water drainage is created by laying insulation in layers of different thicknesses;
- The heat insulator is protected from above cement screed, reinforced mesh or tiled.
Examples of private houses
There are many supporters of flat roofs among developers. They are attracted by the ease of construction, low cost of work and the possibility of placing a site for summer recreation.

A thick layer of snow on a flat roof is not a problem, but additional insulation
The design of buildings with such a roof fits perfectly into the style of minimalism, providing project developers with a wide field for creativity.

Spacious, comfortable and nothing superfluous is the motto of everyone who chooses a house with such a roof. A pitched roof visually weighs down the building, while a flat roof, on the contrary, makes it light and airy.

External view of the facade one-story house with a flat roof compares favorably with the rather boring variations of the “teremkovy” character.

On it, most often you will not see gutters and pipes, the water from which gets on the walls and spoils the appearance of the finish. Internal drainage is efficient, practical and invisible.
For many people, the name “flat roof” is associated primarily with multi-storey buildings. A flat roof - the pros and cons of which we will consider in this article - was practically not used in low-rise construction a dozen years ago. However, today the creation of such a roof in country house is not a problem: modern materials and technologies make it possible to create a flat roof with appropriate consumer characteristics and at an affordable price.
- A flat roof is significantly smaller in area than a pitched roof, which allows you to save on materials and construction work.
- Thanks to the relatively smaller area of the flat roof, it is possible to optimize costs.
- The construction of a flat roof is carried out easier and in a shorter time, compared to a pitched roof, since the necessary materials for installation are located right at the feet of the workers on a flat surface. The same can be said about the repair and maintenance of a flat roof - working on an almost horizontal roof is incomparably more comfortable than on a sloping one.
- On a flat roof, installation and subsequent service work with all kinds of equipment (air conditioning systems, solar panels, antennas, etc.) is more convenient.
- The use of a flat roof is an opportunity to obtain additional useful territory, which can be used as a place where you can relax in the fresh air, play sports, create a garden, flower garden, etc. Today, there are technologies that make it possible to cover the roof even with paving slabs or paving stones. Roof, paved beautiful tiles, in combination with green lawn, garden furniture, a gazebo and a fireplace, can become a place for a comfortable family vacation.
Houses with flat roofs are very popular now
A flat roof, in addition to its advantages, has a number of disadvantages:
- As a result of heavy snowfalls on flat roofs A lot of snow accumulates, which when melted often causes leaks.
- Sometimes the use of internal drains is required.
- There is a risk of the internal drain becoming clogged or freezing.
- There is a need for mechanical cleaning of the roof from too large accumulations of snow.
- Regular monitoring of the moisture content of the insulation and the tightness of the roof is necessary.
Types of flat roofs
There are four types of flat roofs:

Flat roof base
In accordance with building codes, a flat roof, the pros and cons of which we discussed above, must have a base in the form of reinforced concrete floor slabs or corrugated sheets.
Subtleties of waterproofing
Durability roofing structure and its resistance to various negative influences depends on the use of special mixtures and technological processes production of roofing materials. Depending on the roofing materials, they are usually divided into three categories:
- Bitumen roofs, as well as polymer-bitumen based on roofing felt. These materials are available due to their low cost. Fused bitumen-polymer compositions are rolled waterproofing and roofing sheets based on synthetics, on both sides of which a special bitumen is used that retains elasticity even at extremely low temperatures (down to -50 degrees Celsius). During the installation of waterproofing, carried out using gas burners, the rolls are fused together. Roof waterproofing can also be carried out with self-adhesive materials based on polymers and bitumen. IN in this case The mastic is applied to the bottom surface of the roll and, when treated with a solvent, acquires the properties of glue. The disadvantage of bitumen roofing is its fragility.
- Membrane roofs with a base made of foil, rubber or polymers. This material has solid strength and is resistant to fire and other negative environmental influences. The membranes are glued to the screed or simply lie on the base, being loaded with ballast, or are attached mechanically or using glue. To connect membrane sheets, special welders, holding the material together with hot air.
- Roofs based on liquid polymers, which after cooling do not form seams. Such materials are especially often used for structures with complex geometries.

It is very important to do proper waterproofing flat roof
Whatever material is chosen, the joints between the rolls and the junctions with various roof elements must be waterproof. One of the main components of a successful waterproofing device is a high-quality sealant. During the period of operation, the roof is subject to negative influences of the external environment (moisture, hail, stones, strong temperature changes, etc.). Therefore, a high-quality sealant must be resistant to mechanical and temperature influences.
Mastic is usually used as a sealant - putty, which is based on elastic polyurethane resins. After application to the roof, the mastic polymerizes, resulting in the formation of a continuous rubber-like membrane that has waterproofing properties and protects the roofing from mechanical damage.
Mastic is ideal for flat roofing, it is safe, has high adhesion to building surfaces, and is highly resistant to ultraviolet radiation, precipitation and all kinds of microorganisms. It is applied with a brush, roller or airless spray - in two multi-colored layers, which allows you to control the quality, layer thickness and uniformity of distribution of the sealant.
How to arrange water drainage
Regardless of the materials used, a flat roof must have a certain slope to drain water (usually within 3-5%) that appears on the roof as a result of precipitation. The drainage system should be thought out at the building design stage. Gutters determine how effectively moisture will be removed from the roof surface. To prevent gutters from freezing in winter, they are equipped with special thermal cables.

Drains can be organized, when both external and internal water supply is created, and unorganized. When creating an internal water supply system, the roof surface is divided into approximately equal parts of 150-200 square meters each. In places with a slope, drainage funnels are installed, equipped with baskets for catching debris. Typically, funnels are located in the center of the roof, and the pipes are located inside the building.

Rules for insulation and vapor barrier of a flat roof
A flat roof needs insulation. In the absence of a layer of thermal insulation, condensation forms on the roof surface as a result of the contact of warm air masses and the cold surface of the roof. Condensation appears as water stains on the ceilings of the house, and the roof structure gradually collapses.
The roof design involves a base on which a layer of vapor barrier material is laid. The function of a vapor barrier is to protect the insulation from diffuse moisture coming from the premises of the building. The vapor barrier layer includes fiberglass reinforced membrane (based on bitumen and polymers) or vapor barrier film. The layer is laid on top of the screed, and along the edges of the roofing structure it is placed vertically to a height exceeding the height of the insulating material. The seams are sealed.

Insulation is placed above the vapor barrier layer, and a bitumen-based waterproofing carpet is placed on top of it. If expanded clay is used as insulation, then it is necessary to make a cement screed over it, then laying a couple of layers of waterproofing. If the roof is planned to be light (in the case where significant loads are not expected on it), then the waterproofing is simply glued along the entire perimeter of the roof.
For roofs without attics, both external and internal method insulation. The external method is used more often, as its execution is simpler. There are two options for thermal insulation: double-layer and single-layer. The decision about which option to use in practice depends on heat engineering calculations and roof strength requirements. Thermal insulation slabs are placed on the roof structure based on the principle of “staggered seams”. With a two-layer coating of thermal insulation, the joints of the lower and upper slabs are also separated. In the area where the slabs adjoin the parapet, lanterns and walls, thermal insulating edges are created. Thermal insulation materials are attached to the base mechanically(screws, dowels), ballast (pebbles, paving slabs) or glue.
Features of roof ventilation
The roof structure must be equipped ventilation system. As a result of a violation of the tightness of the vapor barrier layer, moisture enters the insulating layer. A thick layer of waterproofing prevents evaporation from occurring, and moisture accumulates in the insulation. As a result, the material loses its insulation characteristics, and moisture appears on the ceilings of the building in the form of stains. In addition, water causes the waterproofing to swell, and at low temperatures, freezing water tears the waterproofing material away from the base. Temperature changes and mechanical damage contribute to the formation of cracks in the roof, which results in roof leaks.

To avoid these problems, the roof must “breathe”. For this, aerators are used - special devices in the form of plastic or metal pipes. They are covered with umbrella caps and are evenly distributed throughout the entire roof area, gravitating towards its highest points. The aeration mechanism works based on the principle of different pressures, which are created by air flows, removing excess moisture vapor from under the roof and preventing water bubbles from forming.
The installation of a roof is a responsible technological operation. Any, even minor, mistake in the design or construction of a roof can cause it to leak in the future. Therefore, when creating a roof, you need to pay attention Special attention the correct selection of hydro- and thermal insulation materials, accurately calculate the upcoming loads on the roof structure, and also select a team of competent builders.

































Durable reliable roof protects a private home from rain, snow, wind and scorching sun, maintains warmth and comfort indoors. And beautiful - gives the architectural appearance of the entire building completeness, uniqueness and expressiveness.

Which roof to choose for your home
The roof is built for more than one decade, so during its entire service life it must meet the requirements of safety, durability and functionality. Construction standards have been developed - SNiP, regulating the main characteristics of structures, rules for calculation and installation of roofs.
The construction and design of the roof are related to the overall architectural design of a private house and are developed at the design stage. The climate zone, type of covering, materials used for the supporting system and roofing determine which roof to choose for your home. High-quality installation work will allow the structure to operate for a long time and avoid costly repairs.

Construction projects for private houses, developed by architectural bureaus, contain ready-made roof solutions for standard construction. The customer can order an individual option that will take into account everything necessary requirements and wishes.
The design and material for manufacturing the enclosing structure depends on its spatial solution. What roof to choose for a private house? Most commonly used pitched forms, less often flat.
Classification of pitched roofs
A slope is a roof plane installed with a slope. According to the number and location of inclined parts, there are varieties:
Single-pitch
The roof plane has a one-sided slope with an angle of up to 30°, along which drainage is carried out. This type is used to cover small buildings or outbuildings. The advantage of coatings is their high resistance to wind loads, the disadvantage is that snow accumulates on the surface and water does not drain well.

Gable
In such structures, the rectangular roof planes are directed in opposite directions at inclination angles of 20-42°. Snow and water do not linger on the surfaces. With a greater slope, the windage of the roof increases, which can lead to its tearing off during strong gusts of wind.

Hip
They are called hipped. One pediment - the triangular part of the facade - is completely or partially replaced with a slope - a hip. The shape is more resistant to wind loads than the gable shape. Its varieties are half-hip Dutch with a shortened hip and hipped, where the slopes in the form of triangles are located at one angle, connecting at the top point.

Multi-pincer
The complex design combines three or more gable forms that cover houses with extensions and highlight an attic area with windows. The gables - pediments - are located parallel and perpendicular to each other. An effective roof is labor-intensive to construct and requires higher flow materials, careful execution of joints.

On our website you can find contacts of construction companies that offer roof repair and design services. You can communicate directly with representatives by visiting the “Low-Rise Country” exhibition of houses.
Attic
The space under the roof is used for housing or economic purposes.

Conical, dome or bell-shaped
Roofs of this configuration cover buildings that are round in plan. Due to the high cost of construction, they are found mainly in elite mansions, religious buildings and stylized buildings.

Pyramidal or spire-shaped
They are used for regular polygonal buildings and have an elongated shape. They decorate the building more than protect it from precipitation.
Flat roofs
Over the past decade, flat roofing has ceased to be a feature of multi-story or industrial construction. Projects of private houses play up the advantages of roofs without a slope. They are equipped with terraces, recreation areas, solar panels, antennas, and climate control equipment.
In fact, the structure is not completely flat; it has a small slope angle - up to 5°. This allows rain and melt water to flow through an organized internal or external drain. The slope is formed due to the different thickness of the screed.

Flat roofs have advantages over spatial coverings:
- original and fresh design;
- the roof can be used;
- the attic space is used as a full floor;
- increased resistance to wind loads.
The main problem that was previously encountered during operation was the insufficient service life of waterproofing. When the protective layer was destroyed, water flowed freely into the room.
Modern materials and technologies make it possible to construct durable flat roofs with guaranteed operation for 50 years. Whatever the manufacturers’ promises, special care must be taken during installation when sealing joints and installing drains.
Disadvantages of a flat roof:
- snow accumulation;
- the need for regular maintenance;
- increased risk of leaks;
- icing of drainage basins in winter.
A flat roof is suitable for individual construction in areas with a mild climate and little rainfall. If there is a lot of snow and frequent rain showers, then the best option will be the choice of design with slopes.
Pitched roof installation
The rafter system is the supporting frame of the roof. It consists of elements:
- Mauerlat - beams on which the entire structure rests. It is mounted along the perimeter of the walls in the upper part.
- Rafter legs- inclined elements placed in increments of up to 1 m and connected to each other by horizontal girders. They can be hanging or layered depending on the type of support.
- Ridge - the top of the roof, the horizontal beam to which the rafters are attached.
- Sheathing or decking is a supporting structure for the “roofing cake”, adding stability to the rafter system.
- Roofs - an external covering consisting of layers of insulation, hydro- and vapor barriers, wind protection, and roofing material.
- Racks, struts, crossbars - vertical, horizontal and diagonal connections that give the frame rigidity and stability.
- Valleys, valleys - connecting elements at the intersections of roof planes.
- Overhangs are extensions of slopes beyond the outer walls.

Diagram of a gable roof
The rafter system for private construction is usually made of wood. The material is accessible and easy to process. It is lightweight and quite durable. You can create any spatial frame without making the system heavier.
Roofing materials are varied. To choose which roof is best for a private home, you need to know the features of their application.
Criterias of choice
When selecting roofing material for covering, consider the possibility of using it from several angles:
- Roof slope. There are manufacturer-recommended tilt angle sizes at which the material will effectively perform its functions.
- Specifications- durability, weight, strength, safety, fire resistance.
- Noise - some materials, for example, metal sheets, can resonate and amplify impact noises from falling drops of rain, hail.
- Financial inclusion.
- Possibility of do-it-yourself installation if self-construction is planned.

The enclosing structure must fit into the overall architectural solution in style, to harmonize with the surrounding landscape.
Materials for various types of roofing
For pitched roofs with a slope angle of 12-45°, the following materials are used:
Folded metal sheets
Made from steel, copper, titanium-zinc or aluminum. Fastening to each other is carried out using a fold - a special type of seam made by hand, mechanical devices or self-latching. The roof is light, strong, durable, there is virtually no waste after installation, and no components are needed. Required for production special tool. The main disadvantage is increased noise. This can be eliminated by installing sound insulation. Steel sheets are susceptible to corrosion.

Corrugated sheet
Rental from polymer coating painted in different colors, durable, non-flammable, durable. The dimensions of the sheet allow you to quickly cover even large spans. A good combination of quality and price.

Metal tiles
Successfully imitates expensive natural material. Among the shortcomings - common to metal surfaces noise, high thermal conductivity. Advantages - affordable price, decorativeness, ease of installation, durability.

Other materials
For slope angles of more than 12°, bitumen and ceramic tiles, slate, and fiber-cement sheets are used.
Slate and piece tiles require a greater slope - from 25°. This will allow water to drain without lingering on the surface, and will protect the roof from leaks at joints and overlaps.

Flat roofs are covered with rolled built-up or mastic self-leveling materials. The first type includes roofing felt, roofing felt, and glassine. Their main disadvantage is their low resistance to frost, UV radiation, and mechanical stress. Reapplication is required every 5-15 years.
Modern analogues - fiberglass, isoplasts, special polymer membranes - far exceed the previous generation in these indicators roll materials, protecting the roof for up to 50 years without repair.
Video description
Even more information about available materials for roofing, which are offered at Russian market, you can watch in this video:
Wooden house - features of choosing a roof
Tree - perfect material for housing construction. It is warm, environmentally friendly, aesthetically comfortable. It is easy to breathe in such a house, because... wooden walls have good vapor permeability. But they cannot boast of high fire resistance, like, for example, brick or reinforced concrete, even with repeated treatment with fire retardants.
Which roof to choose for a wooden house in order to preserve the aura of the natural material and at the same time protect yourself from the possibility of fire?

Fire-resistant roofing materials include:
- ceramic and cement-sand tiles;
- metal coatings;
- asbestos cement sheets.
It is not worth covering wooden houses with materials containing bitumen and its derivatives - bitumen shingles, euro slate, because... Their flammability is average (group G3). They self-ignite at temperatures of 250-300°, releasing toxic substances that are hazardous to breathing.
Asbestos-cement slate, widely used in private construction, is not flammable, but when heated to high temperatures, the corrugated sheets explode and fragments fly in different directions.
Conclusion
There is an answer to the question of which roof is best for a home: it must be safe, reliable, and resistant to cold, heat, wind and water. And at the same time it will please the eye for a long time.
Flat roofs are in demand in modular construction. Among the advantages of this method are the affordable cost and high speed of construction of housing, as well as the possibility of gradually increasing its area
Architects and developers are attracted to these unusual buildings, where you can equip an observation deck or even set up a real hanging garden. Of course, in practice everything turns out to be more complicated than in theory.
Designing a flat roof raises many questions regarding its cost, choice of materials for insulation and waterproofing, organization of water flow, maintenance, etc. Finding answers to them is not so easy. The fact is that domestic contracting companies working in the field of cottage and rooftops are well familiar with the most popular design - pitched, but, as a rule, they have no experience in constructing flat roofs, which are designed completely differently.

Flat roof cost
What immediately attracts attention is the fact that the area of a flat roof is smaller than a pitched roof, which means that less materials will be required, and the work will be cheaper. However, this statement is only true for regions with warm climates and low snow load, moreover, if we are talking about an unused roof. IN middle lane In Russia, to ensure the reliability and durability of a horizontal roof, it is necessary to use quite expensive engineering solutions.
Beam floor
In principle, when constructing a floor, you can use a combination of beams (wooden, steel) and load-bearing corrugated sheeting. However, experts do not recommend using wooden beams (with the exception of those made of LVL beams with a cross-section of 200 × 100 mm) in regions where the snow pressure exceeds 1.2 kPa (about 120 kgf/m2) - that is, in most of the territory of the Russian Federation. A roof covering made of steel I-beams and corrugated sheets with a wave height of 60 mm and a wall thickness of 0.7 mm allows you to cover a span of up to 12 m and can withstand a pressure of at least 6 kPa. But in general, it is less durable than concrete, and is relatively rarely used in individual construction. It makes more sense to use corrugated sheets as permanent formwork, which, by the way, does not replace the need to build a reinforcement cage.

It turns out that 1 m2 of flat concrete or steel base, load bearing capacity which will allow you to withstand the weight of the snow cover, costs 2–2.5 times more than a wooden beam structure of a pitched roof. The difference in the volumetric consumption of insulation is leveled due to the fact that a flat roof requires more expensive material high density. There is still hope to save on roofing, but modern polymer membranes - the optimal waterproofing for horizontal roofs - are no cheaper (and sometimes much more expensive) than flexible tiles. There is no need to install snow guards, but without a roof hatch and drainage system not enough. If you try to cut costs according to the estimate, you will subsequently have to pay the price of having to repair the roof every 10–15 years.
The durability of a flat roof largely depends on the ability of the load-bearing base to withstand operational loads without significant deformation
Finally, it should be taken into account that flat roofs are appropriate only on houses of modern architecture - with large area glazing and sophisticated finishing with the latest facade materials. Both will not be cheap at all.

On a solid foundation
As a rule, in low-rise housing construction, the flat roofing is a prefabricated or monolithic reinforced concrete slab. Reinforced concrete slabs(PB, hollow PC, PV, etc.) are capable of covering a span of up to 9 m in length and can withstand pressure of 8, 9 or 12.5 kPa (this value is indicated by the last digit in the product labeling). They can serve as a “base” for any roofing pies, including those with a top layer of paving slabs or fertile soil. However, to install the structure, it will be necessary to ensure that a truck crane can enter the site (while steel beams and the flooring is easy to lift using winches). The depth of support of the ceiling on the wall depends on the material of the latter - for example, for brick this parameter should be equal to the thickness of the slab. Before proceeding with the installation of the roof, it is important to seal the joints of the elements with mortar and additionally seal them with elastic polymer tape.

The main advantage of membranes based on artificial rubber is that they retain elasticity at low temperatures, that is, they can be installed in winter
Classification of flat roofs
Flat roofs are divided into unused and used. The former visit only for inspection, prevention and repair; for this purpose, a roof hatch is installed, to which it leads attic staircase. The roof in use in cottages most often serves as a terrace, that is, a durable wear-resistant coating must be laid on it, and the load-bearing base is designed for increased loads. A type of exploitation is a roof with landscaping, laid with a turf layer on top of the main heat-waterproofing pie; Usually there are paths and a recreation area on it. A convenient exit to the roof in use should be provided, for example from a vestibule superstructure.
A monolithic reinforced concrete floor is erected from heavy concrete using removable (for example, from OSB boards on jack stands) or permanent (from corrugated sheeting) formwork. It is reinforced with a two- or four-level welded frame made of rods with a diameter of 12 mm. The dimensions of a monolithic slab are not regulated (unlike a prefabricated one), which provides the architect with freedom when designing a building; other advantages are the absence of seams, the comparative simplicity of the installation of passage units (chimney, ventilation ducts) and high load-bearing capacity (subject to compliance with technological regulations).

Roof protection from cold and heat
In the low-rise sector, mostly flat roofs without attics are in demand, because the attic requires additional costs and disrupts the architectural proportions of the house. This means that the roof must protect against winter cold and summer heat. A common feature of flat roofs is that the heat-insulating layer is located on top of the supporting structure (in pitched roofs it is usually located between the rafters). If you insulate the room from below, the dew point may shift into the thickness of the ceiling, which will lead to a reduction in the service life of the latter.

Mastics should be used primarily on roofs of complex configurations
As for roofing options, there are dozens of them. Suffice it to say that more than 40 “recipes” are given in SP 17.13330.2011 alone. At the same time, companies producing coatings and insulation materials are offering more and more new engineering solutions. However, they are always based on one of two fundamental schemes - traditional or inversion.
TechnoNIKOL roof installation diagrams

“TN-ROOF Terrace”: 1 - ceiling; 2 - vapor barrier; 3–5 - EPPS (including the slope-forming layer); 6 - fiberglass; 7 - LOGICROOF V-GR membrane; 8 - geotextile; 9 - tiles on supports
The traditional design in general terms is as follows: laid on top of the supporting base vapor barrier film(polypropylene, polyethylene, butumen-polymer), followed by insulation, for example - slabs from mineral wool, having a compressive strength at ten percent deformation of at least 30 kPa, in one or two layers with a total thickness of 200 mm. Above is a separating layer (for example, made of polyethylene film), along which a reinforced slope-forming screed is poured (a flat roof must be given a slope of 2-3% towards the center or edges to ensure water drainage). The dried screed serves as the basis for a roll or mastic waterproofing coating.
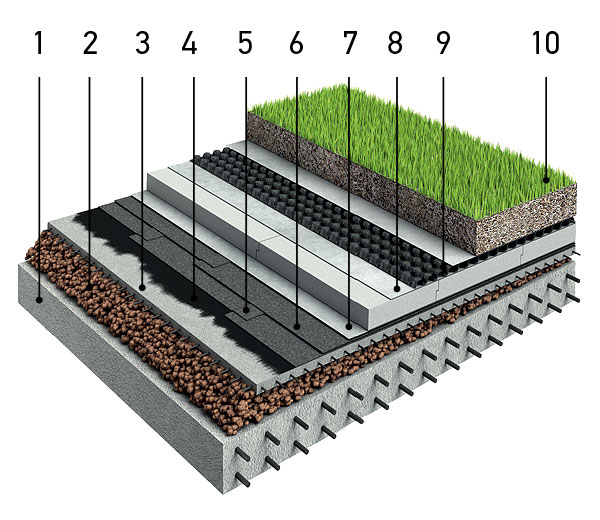
“TN-ROOF Green”: 1 - overlap; 2 - ramp made of expanded clay; 3 - reinforced screed; 4 - bitumen primer; 5 - “Technoelast EPP”; 6 - “Technoelast Green”; 7 - geotextile; 8 - EPPS; 9 - PLANTER GEO membrane; 10 - fertile layer
Other options are also possible. For example, a slope-forming screed can be located at the very bottom of the pie; in this case, the roofing waterproofing is fixed with gravel ballast, paving slabs on supports or special dowels. Some materials, say the “RUF SLOPE” system (Rockwool) or “TechnoNIKOL Slope” allow you to do without a screed altogether: the slabs have variable thickness, and with their help it is not difficult to create smooth changes in level to ensure water drainage.
An inversion roof is designed differently: in it, insulation resistant to constant exposure to water (usually extruded polystyrene foam - EPS) is located on top of the waterproofing. At the same time, the latter is reliably protected from mechanical damage and is located in the positive temperature zone (freezing-thawing cycles are destructive for almost any material). It is easy to turn an inversion roof into a usable one, for example, by covering the insulation with a drainage layer of sand and gravel and laying paving slabs. The disadvantages of the design include more complex drainage. However, we need to talk about gutters separately.
There are special requirements for thermal insulation for flat roofs. The material must not only have a low thermal conductivity coefficient, but also have good resistance to mechanical loads - both distributed (pressure from the overlying layers of the roofing pie, equipment, snow) and local ones that arise during installation. In addition, it is important that the material has hydrophobic properties and is non-flammable. At the moment, there are several ways to install thermal insulation: using mechanical fasteners, adhesive and free laying. In addition to traditional two-layer insulation, single-layer installation is becoming an increasingly popular solution. Rockwool offers unique dual-density slabs that consist of a rigid top layer and a lightweight bottom layer, which speeds up work and improves its quality.
Grigory Gromakov
Specialist in development of the “Flat roofing” direction of the ROCKWOOL company
Water drainage on a flat roof
The flat roof is equipped with a parapet (attic) 30–90 cm high, which helps ensure an organized roof; on a roof in use it also serves as a safety fence. At the same time, the design of gutters should be approached very responsibly, because in case of an error, a huge puddle can form above your head, which can also lead to damage to supporting structures.
As a rule, the choice is made in favor of an internal drain. Such a system is less exposed to the atmosphere and is therefore more durable and reliable than an external one. Let's talk in more detail about its main elements.
Water intake funnels are installed on low areas of the roof. As a rule, on roofs with an area of up to 150 m2, two funnels are installed - the main one, connected to the riser, and the emergency one - with water discharged through a hole in the parapet. With an increase in the number of funnels and risers, the reliability of the system increases, but its cost also increases.
For inversion and green roofs, special funnels with drainage rings have been developed to collect moisture from the intermediate layers. Water receivers must be equipped with electric heating based on a self-regulating cable - then they will properly perform their function during alternating thaws and frosts.

Traditional covering with external drainage 1 - ceiling; 2 - slope-forming screed; 3 - vapor barrier; 4, 5 - mineral wool insulation; 6 - waterproofing; 7 - drain
In a new type of system, the so-called siphon-vacuum system, special funnels are used to prevent air from being sucked into the water flow. Thanks to them, the speed of fluid movement in the pipe (and hence the throughput of the latter) increases, which makes it possible to reduce the diameter of the system elements. However for low-rise buildings the savings turn out to be insignificant, moreover, such systems require more accurate calculations than gravitational ones.
The drainpipe is made from sewer pipes - polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride, and it makes sense to use sound-absorbing products, for example RAUPIANO Plus (REHAU), or soundproof the riser, otherwise you will hear the murmur of water for hours. The riser is connected to the funnel using an elastic coupling. When laying pipes, the number of bends and the length of horizontal sections that reduce throughput systems.
A drainage pipe laid in the basement or insulated underground connects the riser to the rainwater drainage system or ensures the discharge of water into a linear drainage tray. In the second case, there is a risk of clogging the outlet with ice, so the riser should be equipped with a “winter” outlet to the domestic sewer (the latter should be equipped with a water seal). The outlet pipe is cleaned through a collapsible connection or an inspection module.

Drawing: Vladimir Grigoriev/Burda Media
Inversion roof covering with internal drainage 1 - screed; 2 - PVC membrane; 3 - EPPS; 4 - funnel with drainage ring; 5 - drainage membrane; 6 - sand; 7 - paving slabs
When choosing the standard size of elements of a traditional gravity system, they proceed from the intensity of rain in a given area, focusing on SP 32.13330.2012.
The external drainage system is more vulnerable than the internal one, and also affects the appearance of the facades, but it does not require holes in the roof and ceilings and does not eat up the usable area of the house. Water is discharged through parapet funnels or pipes embedded in the parapet, under which classic funnels (like on a pitched roof) and down pipes attached to the walls with brackets are installed. When calculating, it is assumed that for every square meter of roof area there should be 1–1.5 cm2 of the cross-section of drainpipes. Elements of the external system can be made of PVC, steel, copper, zinc-titanium.
For roofs in use, as well as roofs installed in regions with harsh climatic conditions, the inversion scheme is ideal. Since the waterproofing layer is located under the thermal insulation layer, it is protected from mechanical stress, as well as from temperature changes and UV radiation, which significantly extends its service life roofing system. Waterproofing materials based on modified bitumen, it is necessary to lay at least two layers - this technology is more common, and in addition, it allows you to level out possible errors when fusing the material. One layer is enough for a polymer membrane, and reliability is ensured by automatic welding equipment, which greatly increases the speed of work. In addition, when installing a polymer membrane, an open flame is not used, so the technology is considered safer.
Dmitry Mikhailidi
Head of the Engineering and Technical Center of the Technical Directorate of the TechnoNIKOL Corporation
Roof landscaping
Since ancient times, turf-covered roofs have been used in countries with moderately cold and humid climates, and green carpet performed the main moisture-protective function in them.
Within modern concept green roof, a layer of fertile soil with plants is needed to give unusual features to the appearance of the building, decorate the terrace roof and extend the service life of the coating by covering it from ultraviolet rays. In addition, it absorbs rainwater, unloading the gutters, dampens the sound of rain, protects the rooms on the upper floor from overheating in the summer and reduces heat loss in the winter. It is believed that landscaping almost doubles the life of a roof. Its disadvantages include increased load on bearing structures buildings and increasing construction costs. In addition, a green carpet needs care, the intensity of which depends on the selected plant species. If you do not pay due attention to the plants, they will freeze and die from drought.
To green the roof, you should lay on top of the main waterproofing layer (in an inversion scheme - on top of the insulation) an additional cake made of materials that will ensure protection of the waterproofing layer from roots, filtration and drainage of rainwater. For these purposes, special films, dense geotextiles, gravel backfill or drainage and moisture storage membranes made of high-density polyethylene, for example PLANTER GEO or Delta-Floraxx.
Then a mixture of minerals and fertilizers is poured - the so-called soil substrate. You can prepare it yourself by adding fine expanded clay (5–15%), sand (about 20%) and fertilizers to a light soil mixture of neutral peat. As for plants, the easiest way is to limit yourself to meadow forbs and drought-resistant ground covers - sedum, herbaceous carnation, thyme. They do not need to organize an irrigation system, and the thickness of the soil layer can be only 6–12 cm (this type of roof is called extensive). If you plan to walk on the roof among ornamental shrubs, you will have to provide irrigation and increase the soil thickness to 20–40 cm. Such a roof is called intensive, it creates a significant additional load on the ceiling, therefore it must be provided for at the design stage of the building.
The terrace design provides convenient communication between the living quarters of the cottage and the exploited roof, which serves as a resting place

Rolled materials based on modified bitumen are usually fused gas burner, while it is difficult to prevent minor flaws that can cause leakage (if the second layer is missing)
Rolled PVC membranes , for example, Sikaplan WP, Logicroof, Ecoplast are strong and durable (up to 30 years without repair) and do not support combustion. However, they require a professional approach to installation (the joints of the strips must be carefully welded with hot air) and are relatively expensive - from 320 rubles. for 1 m2. It is important to consider that this material does not tolerate contact with bitumen.
Rolled membranes made of ethylene-propylene rubber (EPDM) and thermoplastic polyolefins (TPO) , for example Firestone RubberGard, Logicroof P-RP, retain elasticity at low temperatures. Note that EPDM membranes are highly flammable (class G4) and are designed mainly for use in the construction of an in-use roof, where the waterproofing is covered with tiles, gravel or soil. EPDM and TPO membranes cost 1.3–1.5 times more than polyvinyl chloride membranes (mostly imported products).
Polymer-bitumen mastics allow you to create a seamless coating, but they can only be applied to a durable, non-cracking base - a floor slab or carefully reinforced screed, and this process is quite long and laborious. The service life of a two-layer coating with a thickness of 5 mm is about 20 years, the price is from 120 rubles. for 1 m2. In practice, mastics are used mainly for roof repairs and gluing rolled materials.
Polymer and cement-polymer self-leveling waterproofing
, say Aquascud, Osmolastic, Osmoflex, is highly elastic
and UV resistance. To improve characteristics, materials are used in combination with special primers and lining films, reinforced mineral fiber(all components are supplied complete as a single system). The estimated service life of the coating is more than 50 years; price - from 700 rub. for 1 m2.
Flat roof: a pragmatist's view
| Advantages | Flaws |
|---|---|
| Eliminates snow avalanches and reduces the risk of falling ice. | Requires significant costs to construct a foundation with high load-bearing capacity. |
| Provides convenient access to chimneys, ventilation risers, antennas; Compared to pitched ones, it is easier to maintain and repair. | It is more susceptible to atmospheric factors than pitched, so durability is guaranteed only if expensive materials are used. |
| Can serve as a recreation area or terrace. | Requires increased attention to the arrangement and condition of the drainage system (especially with internal drainage). |
| Slightly less susceptible to wind loads than pitched. | |
| Allows you to implement the principle of phased modular construction (to make an extension to a house with a pitched roof, you need to solve a difficult architectural and design problem). |
The shape of the roof, as well as the type of its covering, influence the design of the house as a whole. But the roof is not only a decoration for a residential building, it is also its safety, thermal insulation and protection from any weather influences. To make your home cozy and comfortable, you need to approach the choice of roofing wisely.
There are two main forms of roofs that are used in cottage construction: pitched and flat. There is no universal answer to the question of which one is more practical and safer - each has its own advantages and disadvantages.
A pitched roof is a roof whose surface is inclined towards the outer walls. The slope of such roofs can vary from 5 to 90 degrees. Variety of species pitched roofs And roofing materials makes it possible to realize the most daring architectural ideas when designing cottages.
The main advantage of a pitched roof is that, due to the slope, it ensures accelerated water drainage. In addition, there is an attic underneath, which provides an air gap that reduces heat loss through the roof.
However, a pitched roof has a higher cost due to the need to create a rafter system, and since it is part of the overall facade, it requires more expensive materials. Pitched roofing is difficult to maintain: in order to safely move along its surface, additional equipment is required - stairs or fences. The steeper the slope of a pitched roof, the higher the cost of repairing it.
The simplest material for finishing such a roof is slate (from 100 rubles/m²), but it has disadvantages - it leaves a lot of debris, absorbs moisture and quickly deteriorates, and this material is also harmful to health. However, Russian slate factories are still operating at full capacity.
The most widely used materials in the mass cottage construction market are those in the price niche from 150 to 400 rubles/m²: metal tiles and various bitumen coatings.
Metal tiles have gained a leading position due to their affordability and decent aesthetic appearance. Among its obvious advantages are cost-effectiveness, long service life (up to 50 years), and low weight, which does not create additional load on the walls of the building. In addition, it is resistant to external factors and various kinds mechanical damage, and is also not afraid of fire. However, there are also disadvantages: corrosion due to improper use, increased noise, high consumption material and poor maintainability. Metal tiles are supplied to our market by domestic companies Metal Profile and Grand Line, as well as imported manufacturers - Ruuki, Metehe OY (Finland), Lindab (Sweden), etc.
Corrugated bitumen sheet, similar in appearance to slate, appeared on our market in the early 90s. It is a mixture of bitumen and cellulose with the addition of thermosetting resin and mineral pigments, durable material(declared service life - up to 50 years), with up to 25 years of warranty from various manufacturers. Sheets of bitumen “slate” do not contain asbestos, which is harmful to health, and are made from environmentally friendly materials, are easy to install and allow installation on the old coating, and in addition, due to the wavy configuration, natural ventilation of the roof is ensured.
 Bituminous (flexible) shingles have all the above-mentioned advantages, but at the same time they have a wide color palette and leave a minimum of waste during production. This material is intended for pitched roofs with a slope from 11.3 to 90 degrees. It consists of fiberglass, impregnated on both sides with bitumen binder, with the addition of rubber or plastic, as well as toppings (slate or basalt). Service life - from 15 to 30 years. Among the most popular brands are single-layer and double-layer flexible tiles KATEPAL, TechnoNIKOL products Shinglas, Tegola, etc.
Bituminous (flexible) shingles have all the above-mentioned advantages, but at the same time they have a wide color palette and leave a minimum of waste during production. This material is intended for pitched roofs with a slope from 11.3 to 90 degrees. It consists of fiberglass, impregnated on both sides with bitumen binder, with the addition of rubber or plastic, as well as toppings (slate or basalt). Service life - from 15 to 30 years. Among the most popular brands are single-layer and double-layer flexible tiles KATEPAL, TechnoNIKOL products Shinglas, Tegola, etc.
Cement-sand tiles will cost from 350 to 500 rubles/m². Her main feature the fact that it gains strength during use. This is a piece product of various shapes and colors, so it can be used to lay complex roofs with virtually no waste. The material is durable, but has a lot of weight and special requirements for the rafter system. The disadvantages include complex installation technology and high cost.
Even more expensive ceramic tiles- from 750 rub./m². Moreover, its service life is from 100 years. It is characterized by a variety of shapes and colors, but at the same time great weight and complexity of installation.
Flat roof
The main advantage of a flat roof is its ability to be used. On the surface of a flat or slightly sloping roof you can place a lawn, recreation area, swimming pool, solarium and much more.
The advantages of such a roof also include convenient installation and ease of maintenance of roof equipment: antennas, air conditioners, solar panels, ventilation shafts, etc. And among the obvious disadvantages is the need for internal drains and regular mechanical cleaning from snow and ice. In addition, constant monitoring of humidity, the condition of the insulation and the tightness of the roof is required.
Not so long ago, flat roofs began to be actively used in low-rise construction; before that, it was the province of multi-story buildings. With the advent of modern roofing materials, it has become possible to provide a flat roof with reliable thermal and waterproofing. When installing a flat roof, you can save on materials and optimize costs due to the fact that its area is smaller than that of a pitched roof.
Another feature of exploited roofs is the need for a rigid base, otherwise the integrity of the waterproofing layer is impossible. The base is a screed made of concrete or corrugated sheeting, which creates a place for drainage. Thermal insulation material on the roof in use, it experiences serious dynamic and static loads and must be strong enough. If the insulation has low rigidity, a cement screed will be needed on top of it.
But unused flat roofs do not need rigid insulation. To service the roof structure, ladders or bridges are constructed to help correctly distribute loads over the roof surface. Unexploited roofs are cheaper to construct, but their service life is shorter than in the case of exploited ones.
One of the most common roofing materials is roofing felt, rolled bitumen materials, and polymer-bitumen technologies. The “Top Tite” elastomeric membranes from KATEPAL and the line of materials from TechnoNIKOL have deservedly gained particular popularity.
Text by Natalia Burkovskaya
